Metropolitan area in the United States
"Chicagoland" redirects here. For other uses, see Chicagoland (disambiguation).
Conurbation in the United States
|
Chicago metropolitan area
|
Chicago–Naperville, IL–IN–WI
Combined Statistical Area |
|
From top, left to right: Chicago skyline from Lakefront Trail at Northerly Island during sunrise, aerial view Evanston, view of Gold Coast, Downtown Naperville, view of Downtown Aurora
|

Map of Chicago–Naperville, IL–IN–WI CSA
Chicago–Naperville–Schaumburg, IL
Elgin, IL Metropolitan Division
Lake County, IL Metropolitan Division
Lake County–Porter County–Jasper Cty, IN
Other Statistical Areas in the Chicago CSA
Kenosha, WI MSA
Ottawa, IL µSA
Michigan City–La Porte, IN MSA
Kankakee, IL MSA
|
City of Chicago
Chicago–Naperville–Elgin, IL–IN MSA
|
|
Country United StatesStates
United StatesStates Illinois
Illinois
 Indiana
Indiana
 WisconsinCore city
WisconsinCore city ChicagoSatellite cities
ChicagoSatellite cities
- - Aurora
- - Elgin
- - Crystal Lake
- - Joliet
- - Naperville
- - Schaumburg
- - Waukegan
- - Kankakee
- - Gary
- - Hammond
- - Michigan City
- - Kenosha
Area
• Metro
10,856 sq mi (28,120 km2)Highest elevation
[1]
673 ft (205 m)Lowest elevation
[1]
579 ft (176 m)Population
• Density886/sq mi (342/km2) • Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) (2022)
9,441,957[2] (3rd) • Combined Statistical Area (CSA) (2022)
9,806,184 [3] (4th)DemonymChicagolanderGDP
[4]
• Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA)$894.862 billion (2023) • Combined Statistical Area (CSA)$919.229 billion (2023)Time zoneUTC−6 (CST) • Summer (DST)UTC−5 (CDT)Area codes219, 224/847, 262, 312/872, 331/630, 574, 464/708, 773/872 and 779/815
The Chicago metropolitan area, also referred to as Chicagoland, is the largest metropolitan statistical area in the U.S. state of Illinois, and the Midwest, containing the City of Chicago along with its surrounding suburbs and satellite cities. Encompassing 10,286 square mi (28,120 km2), the metropolitan area includes the city of Chicago, its suburbs and hinterland, that span 13 counties across northeast Illinois and northwest Indiana. The MSA had a 2020 census population of 9,618,502 and the combined statistical area, which spans 19 counties and additionally extends into southeast Wisconsin, had a population of nearly 10 million people.[5][6] The Chicago area is the third-largest metropolitan area in the United States and the fourth-largest metropolitan area in North America (after Mexico City, New York City, and Los Angeles), and the largest in the Great Lakes megalopolis. Its urban area is one of the 40 largest in the world.
According to the 2020 census, the metropolitan's population is approaching the 10 million mark. The metropolitan area has seen a substantial increase of Latin American residents on top of its already large Latino population, and the Asian American population also increased according to the 2020 Census. The metro area has a large number of White, Black, Latino, Asian, and Arab American residents, and also has Native American residents in the region, making the Chicago metropolitan area population truly diverse. The Chicago metropolitan area represents about 3 percent of the entire US population.
Chicagoland has one of the world's largest and most diversified economies. With more than six million full and part-time employees, the Chicago metropolitan area is a key factor of the Illinois economy, as the state has an annual GDP of over $1 trillion.[7] The Chicago metropolitan area generated an annual gross regional product (GRP) of approximately $700 billion in 2018.[8] The region is home to more than 400 major corporate headquarters, including 31 in the Fortune 500[9] such as McDonald's, United, and Blue Cross Blue Shield. With many companies moving to Chicagoland, and many current companies expanding, the area ranked as the nation's top metropolitan area for corporation relocations and expansions for nine consecutive years, the most consecutive years for any region in the country.[10]
The Chicago area is home to a number of the nation's leading research universities including the University of Chicago, Northwestern University, the University of Illinois at Chicago, DePaul University, Loyola University, and the Illinois Institute of Technology (IIT). The University of Chicago and Northwestern University are consistently ranked as two of the best universities in the world.
There are many transportation options around the region. Chicagoland has three separate rail networks; the Chicago Transit Authority (CTA), Metra, and the South Shore Line. The CTA operates elevated and subway lines that run primarily throughout the city, Downtown Chicago, and into some suburbs. The CTA operates some of its rail lines 24 hours a day, every day of the year, nonstop service, making Chicago, New York City, and Copenhagen the only three cities in the world to offer some 24 hour rail service running nonstop, everyday throughout their city limits. The Metra commuter rail network runs numerous lines between Downtown Chicago and suburban/satellite cities, with one line stretching to Kenosha, Wisconsin, which is part of the Chicago metropolitan area. The interurban South Shore Line runs between Downtown Chicago and the northwest Indiana portion of the metropolitan area. In addition, Amtrak operates Union Station in Downtown Chicago as one of its largest rail hubs, with numerous lines radiating to and from the station.
CTA bus routes serve the city proper, with some service into the suburbs. Pace bus routes serve the suburbs, with some service into the city. In addition, numerous CTA bus routes operate 24 hours a day, nonstop.
Definitions
[edit]
Chicago Metropolitan statistical area
[edit]
 The Chicago–Naperville, IL–IN–WI Combined Statistical Area as defined by the U.S. Office of Management and Budget:
The Chicago–Naperville, IL–IN–WI Combined Statistical Area as defined by the U.S. Office of Management and Budget:
Chicago–Naperville–Elgin, IL–IN–WI MSA
Michigan City–La Porte, IN MSA
Kankakee, IL MSA
Ottawa, IL MSA
The Chicago metropolitan statistical area (MSA) was originally designated by the United States Census Bureau in 1950. It comprised the Illinois counties of Cook, DuPage, Kane, Lake and Will, along with Lake County in Indiana. As surrounding counties saw an increase in their population densities and the number of their residents employed within Cook County, they met Census criteria to be added to the MSA. The Chicago MSA, now defined by the U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) as the Chicago–Naperville–Elgin, IL–IN–WI Metropolitan Statistical Area, is the third-largest MSA by population in the United States. The 2022 census estimate for the population of the MSA was 9,441,957.[11]
The Chicago MSA is further subdivided into four metropolitan divisions. A breakdown of the county constituents and 2021 estimated populations of the four metropolitan divisions of the MSA are as follows:[11]
Chicago–Naperville–Elgin, IL–IN–WI Metropolitan Statistical Area (9,509,934)
- Chicago–Naperville–Schaumburg, IL Metropolitan Division (7,159,394)
- Cook County, Illinois (5,173,146)
- DuPage County, Illinois (924,885)
- Grundy County, Illinois (52,989)
- McHenry County, Illinois (311,122)
- Will County, Illinois (697,252)
- Elgin, IL Metropolitan Division (750,869)
- DeKalb County, Illinois (100,414)
- Kane County, Illinois (515,588)
- Kendall County, Illinois (134,867)
- Lake County, IL Metropolitan Division (711,239)
- Lake County, Illinois (711,239)
- Lake County–Porter County–Jasper County, IN Metropolitan Division (719,700)
- Jasper County, Indiana (33,091)
- Lake County, Indiana (498,558)
- Newton County, Indiana (13,808)
- Porter County, Indiana (174,243)
Combined statistical area
[edit]
The OMB also defines a slightly larger region as a combined statistical area (CSA). The Chicago–Naperville, IL–IN–WI Combined Statistical Area combines the following core-based statistical areas, listed with their 2021 estimated populations. The combined statistical area as a whole had a population of 9,806,184 as of 2022.[11]
- Chicago–Naperville–Elgin, IL–IN–WI metropolitan statistical area (9,509,934)
- Kankakee, IL metropolitan statistical area (106,601)
- Kankakee County, Illinois (106,601)
- Michigan City–La Porte, IN metropolitan statistical area (112,390)
- LaPorte County, Indiana (112,390)
- Ottawa, IL micropolitan statistical area (147,414)
- Bureau County, Illinois (32,883)
- LaSalle County, Illinois (108,965)
- Putnam County, Illinois (5,566)
United Nations' Chicago urban agglomeration
[edit]
The Chicago urban agglomeration, according to the United Nations World Urbanization Prospects report (2023 revision), lists a population of 8,937,000.[12] The term "urban agglomeration" refers to the population contained within the contours of a contiguous territory inhabited at urban density levels. It usually incorporates the population in a city, plus that in the contiguous urban, or built-up area.
Chicagoland
[edit]
 Chicagoland by county and state[13]
Chicagoland by county and state[13]
 A map of Chicagoland in relation to the states of Wisconsin, Illinois, and Indiana
A map of Chicagoland in relation to the states of Wisconsin, Illinois, and Indiana
Chicagoland is an informal name for the Chicago metropolitan area. The term Chicagoland has no official definition, and the region is often considered to include areas beyond the corresponding MSA, as well as portions of the greater CSA.[citation needed]
Colonel Robert R. McCormick, editor and publisher of the Chicago Tribune, usually gets credit for placing the term in common use.[14][15] McCormick's conception of Chicagoland stretched all the way to nearby parts of four states (Indiana, Wisconsin, Michigan, and Iowa).[14] The first usage was in the Tribune's July 27, 1926, front page headline, "Chicagoland's Shrines: A Tour of Discoveries", for an article by reporter James O'Donnell Bennett.[16] He stated that Chicagoland comprised everything in a 200-mile (320 km) radius in every direction and reported on many different places in the area. The Tribune was the dominant newspaper in a vast area stretching to the west of the city, and that hinterland was closely tied to the metropolis by rail lines and commercial links.[17]
Today, the Chicago Tribune's usage includes the city of Chicago, the rest of Cook County, eight nearby Illinois counties (Lake, McHenry, DuPage, Kane, Kendall, Grundy, Will, and Kankakee), and the two Indiana counties of Lake and Porter.[18] Illinois Department of Tourism literature uses Chicagoland for suburbs in Cook, Lake, DuPage, Kane, and Will counties,[19] treating the city separately. The Chicagoland Chamber of Commerce defines it as all of Cook, DuPage, Kane, Lake, McHenry, and Will counties.[20]
In addition, company marketing programs such as Construction Data Company's[21] "Chicago and Vicinity" region and the Chicago Automobile Trade Association's "Chicagoland and Northwest Indiana" advertising campaign are directed at the MSA itself, as well as LaSalle, Winnebago (Rockford), Boone, and Ogle counties in Illinois, in addition to Jasper, Newton, and La Porte counties in Indiana and Kenosha, Racine, and Walworth counties in Wisconsin, and even as far northeast as Berrien County, Michigan. The region is part of the Great Lakes Megalopolis, containing an estimated 54 million people.[citation needed]
Collar counties
[edit]
The term "collar counties" is a colloquialism for the five counties (DuPage, Kane, Lake, McHenry, and Will) of Illinois that border Chicago's Cook County. After Cook County, they are also the next five most populous counties in the state. According to the Encyclopedia of Chicago, there is no specifically known origin of the phrase, but it has been commonly used among policy makers, urban planners, and in the media. However, it also notes that as growth has spread beyond these counties, it may have lost some of its usefulness.[22]
Chicago Metropolitan Agency for Planning
[edit]
Main article: Chicago Metropolitan Agency for Planning
Chicago Metropolitan Agency for Planning (CMAP) is an Illinois state agency responsible for transportation infrastructure, land use, and long-term economic development planning for the areas under its jurisdiction within Illinois.[23] The planning area has a population of over 8 million, which includes the following locations in Illinois:[24]
- Cook County
- DuPage County
- Kane County
- Kendall County
- Lake County
- McHenry County
- Will County
Panorama of North Avenue Beach
Geography and environment
[edit]
Further information: Geography of Chicago
The city of Chicago lies in the Chicago Plain, a flat and broad area characterized by little topographical relief. The few low hills are sand ridges. North of the Chicago Plain, steep bluffs and ravines run alongside Lake Michigan.
Along the southern shore of the Chicago Plain, sand dunes run alongside the lake. The tallest dunes reach up to near 200 feet (61 m) and are found in Indiana Dunes National Park. Surrounding the low plain are bands of moraines in the south and west suburbs. These areas are higher and hillier than the Chicago Plain. A continental divide, separating the Mississippi River watershed from that of the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence River, runs through the Chicago area.
A 2012 survey of the urban trees and forests in the seven county Illinois section of the Chicago area found that 21% of the land is covered by the tree and shrub canopy, made up of about 157,142,000 trees. The five most common tree species are buckthorn, green ash, boxelder, black cherry, and American elm. These resources perform important functions in carbon storage, water recycling, and energy saving.[25][26]
Night aerial view of Chicago and vicinity
Demographics
[edit]
 Taken from the ISS on June 23, 2022; downtown Chicago is at the center by the lake.
Taken from the ISS on June 23, 2022; downtown Chicago is at the center by the lake.
As of 2022, the metropolitan area had a population of 9,442,159. The population density was 1,312.3 per square mile. The racial makeup was 50.1% Non-Hispanic White, 23.4% were Hispanic, 15.5% were Non-Hispanic African Americans, 7.2% were Asian, 0.1% were Non-Hispanic Native American, 0.4% identified as “some other race,” and 3.2% were non-Hispanic multiracial.[27]
According to 2022 estimates from the American Community Survey, the largest ancestries in the Chicago metro area were Mexican (18%), African (17.7%), German (12.8%), Irish (9.9%), Polish (8%), Italian (5.9%), English (5.2%), Indian (2.7%), Puerto Rican (2.3%), Filipino (1.7%), Swedish (1.5%), and Chinese (1.4%).[28][29][30][31]
The suburbs, surrounded by easily annexed flat ground, have been expanding at a tremendous rate since the early 1960s. Aurora, Elgin, Joliet, and Naperville are noteworthy for being four of the few boomburbs outside the Sun Belt, West Coast and Mountain States regions, and exurban Kendall County ranked as the fastest-growing county (among counties with a population greater than 10,000) in the United States between the years 2000 and 2007.[32]
Settlement patterns in the Chicago metropolitan area tend to follow those in the city proper: the northern and northwestern suburbs are generally affluent and upper-middle class, while the southern suburbs (sometimes known as Chicago Southland) have somewhat lower median incomes and a cost of living, with the exception being the southwest suburbs which contain many upper-middle class areas. Another exception to this is the West Side, which has a somewhat lower median income, but the western suburbs contain many affluent and upper-middle class areas. According to the 2000 Census, DuPage County as a whole had the highest median household income of any county in the Midwestern United States, although there are individual cities and towns in other surrounding counties in the metro that have even higher median incomes.
According to 2022 estimates from the U.S. Census, poverty rates of the largest counties from least poverty to most are as follows: McHenry 4.0%, Dupage 6.7%, Will 6.9%, Kane 7.8%, Lake 8.0%, and Cook 13.6%.[33] However, Cook County, which contains luxury high rises and expensive houses in sections of the city and expensive houses along the waterfront in the North Shore area, would also have the highest percentage of expensive homes in the region.
In an in-depth historical analysis, Keating (2004, 2005) examined the origins of 233 settlements that by 1900 had become suburbs or city neighborhoods of the Chicago metropolitan area. The settlements began as farm centers (41%), industrial towns (30%), residential railroad suburbs (15%), and recreational/institutional centers (13%). Although relations between the different settlement types were at times contentious, there also was cooperation in such undertakings as the construction of high schools.[citation needed]
Population
[edit]
As the Chicago metropolitan area has grown, more counties have been partly or totally assimilated with the taking of each decennial census.
| Census Area |
Area Type |
2020 census |
2010 census |
2000 census |
1990 census |
1980 Census |
1970 census |
1960 census |
1950 census |
| Chicago-Naperville-Joliet, IL-IN-WI |
Metropolitan |
9,618,502 |
9,461,105 |
9,098,316 |
8,065,633 |
7,869,542 |
7,612,314 |
6,794,461 |
5,495,364 |
| Cook County, Illinois |
Metropolitan |
5,275,541 |
5,194,675 |
5,376,741 |
5,105,067 |
5,253,655 |
5,492,369 |
5,129,725 |
4,508,792 |
| DeKalb County, Illinois |
Metropolitan |
100,420 |
105,160 |
88,969 |
77,932 |
74,624 |
71,654 |
51,714 |
40,781 |
| DuPage County, Illinois |
Metropolitan |
932,877 |
916,924 |
904,161 |
781,666 |
658,835 |
491,882 |
313,459 |
154,599 |
| Grundy County, Illinois |
Metropolitan |
52,533 |
50,063 |
37,535 |
32,337 |
30,582 |
26,535 |
22,350 |
19,217 |
| Kane County, Illinois |
Metropolitan |
516,522 |
515,269 |
404,119 |
317,471 |
278,405 |
251,005 |
208,246 |
150,388 |
| Kendall County, Illinois |
Metropolitan |
131,869 |
114,736 |
54,544 |
39,413 |
37,202 |
26,374 |
17,540 |
12,115 |
| McHenry County, Illinois |
Metropolitan |
310,229 |
308,760 |
260,077 |
183,241 |
147,897 |
111,555 |
84,210 |
50,656 |
| Will County, Illinois |
Metropolitan |
696,355 |
677,560 |
502,266 |
357,313 |
324,460 |
249,498 |
191,617 |
134,336 |
| Jasper County, Indiana |
Metropolitan |
32,918 |
33,478 |
30,043 |
24,960 |
26,138 |
20,429 |
18,842 |
17,031 |
| Lake County, Indiana |
Metropolitan |
498,700 |
496,005 |
484,564 |
475,594 |
522,965 |
546,253 |
513,269 |
368,152 |
| Newton County, Indiana |
Metropolitan |
13,830 |
14,244 |
14,566 |
13,551 |
14,844 |
11,606 |
11,502 |
11,006 |
| Porter County, Indiana |
Metropolitan |
173,215 |
164,343 |
146,798 |
128,932 |
119,816 |
87,114 |
60,279 |
40,076 |
| Lake County, Illinois |
Metropolitan |
714,342 |
703,462 |
644,356 |
516,418 |
440,372 |
382,638 |
293,656 |
179,097 |
| Kenosha County, Wisconsin |
Metropolitan |
169,151 |
166,426 |
149,577 |
128,181 |
123,137 |
117,917 |
100,615 |
75,238 |
| Kankakee County, Illinois |
Combined |
107,502 |
113,449 |
103,833 |
96,255 |
102,926 |
97,250 |
92,063 |
73,524 |
| LaSalle County, Illinois |
Combined |
109,658 |
113,924 |
111,509 |
106,913 |
112,003 |
111,409 |
110,800 |
100,610 |
| Bureau County, Illinois |
Combined |
33,244 |
34,978 |
35,503 |
35,688 |
39,114 |
38,541 |
37,594 |
37,711 |
| Putnam County, Illinois |
Combined |
5,637 |
6,006 |
6,086 |
5,730 |
6,085 |
5,007 |
4,570 |
4,746 |
| LaPorte County, Indiana |
Combined |
112,417 |
111,467 |
110,106 |
107,066 |
108,632 |
105,342 |
95,111 |
76,808 |
| Chicago-Naperville-Joliet, IL-IN-WI |
Combined |
9,986,960 |
9,686,021 |
9,312,255 |
8,385,397 |
8,264,490 |
8,089,421 |
7,204,198 |
5,911,816 |
Counties highlighted in gray were not included in the MSA for that census. The CSA totals in blue are the totals of all the counties listed above, regardless of whether they were included in the Chicago Combined Statistical Area at the time.[34]
Principal municipalities
[edit]
Over 1,000,000 population
[edit]
Over 100,000 population
[edit]
- Aurora, Illinois (180,542)
- Joliet, Illinois (150,362)
- Naperville, Illinois (149,540)
- Elgin, Illinois (114,797)
Over 50,000 population
[edit]
- Kenosha, Wisconsin (99,986)
- Waukegan, Illinois (89,321)
- Cicero, Illinois (85,268)
- Schaumburg, Illinois (78,723)
- Evanston, Illinois (78,110)
- Hammond, Indiana (77,879)
- Arlington Heights, Illinois (77,676)
- Bolingbrook, Illinois (73,922)
- Gary, Indiana (69,093)
- Palatine, Illinois (67,908)
- Skokie, Illinois (67,824)
- Des Plaines, Illinois (60,675)
- Orland Park, Illinois (58,703)
- Oak Lawn, Illinois (58,362)
- Berwyn, Illinois (57,250)
- Mount Prospect, Illinois (56,852)
- Tinley Park, Illinois (55,971)
- Oak Park, Illinois (54,583)
- Wheaton, Illinois (53,970)
- Downers Grove, Illinois (50,247)
View of Chicago greater metropolitan region and the North branch of the Chicago River from the Willis Tower
Urban areas within
[edit]
Within the boundary of the 16-county Chicago Combined Statistical Area lies the Chicago urban area, as well as 26 smaller urban areas.[35] Some of the urban areas below may partially cross into other statistical areas. Only those situated primarily within the Chicago combined statistical area are listed here.
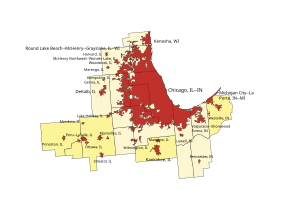 Urban areas contained within the Chicago combined statistical area as of the 2020 census:
Urban areas contained within the Chicago combined statistical area as of the 2020 census:
Urban areas
Counties in the Chicago MSA
Counties in the Chicago CSA but not the MSA
| Urban area |
Population
(2020 census) |
Land area
(sq mi) |
Land area
(km2) |
Density
(population / sq mi) |
Density
(population / km2) |
| Chicago, IL–IN |
8,671,746 |
2,337.89 |
6,055.09 |
3,709.2 |
1,432.1 |
| Round Lake Beach–McHenry–Grayslake, IL–WI |
261,835 |
127.61 |
330.52 |
2,051.8 |
792.2 |
| Kenosha, WI |
125,865 |
56.17 |
145.48 |
2,240.8 |
865.2 |
| Michigan City–La Porte, IN–MI |
71,367 |
49.16 |
127.32 |
1,451.7 |
560.5 |
| Kankakee, IL |
66,530 |
31.66 |
82.00 |
2,101.4 |
811.3 |
| DeKalb, IL |
64,736 |
25.63 |
66.39 |
2,525.6 |
975.1 |
| Valparaiso–Shorewood Forest, IN |
51,867 |
33.64 |
87.12 |
1,542.0 |
595.4 |
| Peru–LaSalle, IL |
29,763 |
21.45 |
55.56 |
1,387.4 |
535.7 |
| Woodstock, IL |
25,298 |
9.31 |
24.10 |
2,718.7 |
1,049.7 |
| Ottawa, IL |
20,122 |
9.99 |
25.87 |
2,014.2 |
777.7 |
| Streator, IL |
16,209 |
8.12 |
21.04 |
1,995.3 |
770.4 |
| Coal City–Braidwood, IL |
15,837 |
10.29 |
26.65 |
1,539.4 |
594.4 |
| Morris, IL |
15,740 |
8.64 |
22.37 |
1,822.2 |
703.5 |
| Lowell, IN |
10,747 |
5.28 |
13.66 |
2,037.2 |
786.6 |
| Manteno, IL |
10,437 |
6.01 |
15.56 |
1,736.8 |
670.6 |
| Harvard, IL |
9,376 |
4.36 |
11.30 |
2,148.7 |
829.6 |
| Princeton, IL |
7,979 |
6.20 |
16.06 |
1,287.1 |
497.0 |
| Marengo, IL |
7,509 |
3.81 |
9.86 |
1,971.5 |
761.2 |
| Lake Holiday, IL |
7,313 |
4.30 |
11.14 |
1,700.5 |
656.6 |
| Mendota, IL |
6,918 |
2.85 |
7.38 |
2,426.2 |
936.8 |
| Wilmington, IL |
6,388 |
3.95 |
10.23 |
1,617.3 |
624.5 |
| McHenry Northwest–Wonder Lake, IL |
5,758 |
2.35 |
6.08 |
2,453.6 |
947.4 |
| Hampshire, IL |
5,699 |
2.72 |
7.06 |
2,091.4 |
807.5 |
| Rensselaer, IN |
5,509 |
3.23 |
8.37 |
1,703.9 |
657.9 |
| Genoa, IL |
5,484 |
2.20 |
5.69 |
2,498.0 |
964.5 |
| Westville, IN |
5,189 |
2.10 |
5.45 |
2,466.0 |
952.1 |
| Marseilles, IL |
4,660 |
2.39 |
6.19 |
1,948.4 |
752.3 |
Economy
[edit]
 Westward view from the Willis Tower in Chicago
Westward view from the Willis Tower in Chicago
Main article: Economy of Chicago
See also: List of companies in the Chicago metropolitan area, Chicagoland Chamber of Commerce, and Economy of Illinois
The Chicago metropolitan area is home to the corporate headquarters of 57 Fortune 1000 companies, including AbbVie Inc., Allstate, Kraft Heinz, McDonald's, Mondelez International, Motorola, United Airlines, Walgreens, and more. The Chicago area also headquarters a wide variety of global financial institutions including Citadel LLC, Discover Financial Services, Morningstar, Inc., CNA Financial, and more. Chicago is home to the largest futures exchange in the world, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange. In March 2008, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange announced its acquisition of NYMEX Holdings Inc, the parent company of the New York Mercantile Exchange and Commodity Exchange. CME'S acquisition of NYMEX was completed in August 2008.
A key piece of infrastructure for several generations was the Union Stock Yards of Chicago, which from 1865 until 1971 penned and slaughtered millions of cattle and hogs into standardized cuts of beef and pork. This prompted poet Carl Sandburg to describe Chicago as the "Hog Butcher for the World".[36]
The Chicago area, meanwhile, began to produce significant quantities of telecommunications gear, electronics, steel, crude oil derivatives, automobiles, and industrial capital goods.
By the early 2000s, Illinois' economy had moved toward a dependence on high-value-added services, such as financial trading, higher education, logistics, and health care. In some cases, these services clustered around institutions that hearkened back to Illinois's earlier economies. For example, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, a trading exchange for global derivatives, had begun its life as an agricultural futures market.
In 2007, the area ranked first among U.S. metro areas in the number of new and expanded corporate facilities.[37] It ranked third in 2008, behind the Houston–Sugar Land–Baytown and Dallas–Fort Worth metropolitan areas,[38] and ranked second behind the New York metropolitan area in 2009.[39]
The Wall Street Journal summarized the Chicago area's economy in November 2006 with the comment that "Chicago has survived by repeatedly reinventing itself."[40]
Transportation
[edit]
The Eisenhower Expressway with the Chicago Transit Authority Blue Line tracks and the non-revenue ramp that leads to the Pink Line
Main articles: Transportation in Chicago and Roads and freeways in Chicago
Major airports
[edit]
- Chicago O'Hare International Airport (ORD)
- Chicago Midway International Airport (MDW)
- Milwaukee Mitchell International Airport (MKE) (located in the adjacent Milwaukee metropolitan area)
- Chicago Rockford International Airport (RFD) (located in the adjacent Rockford metropolitan area)
- Gary/Chicago International Airport (GYY)
Commercial ports
[edit]
- Port of Chicago
- Port of Indiana-Burns Harbor
Transit systems
[edit]
Commercial freight
[edit]
Chicago has been at the center of the United States' railroad network since the 19th century. Almost all Class I railroads serve the area, the most in North America.[41]
Passenger
[edit]
- Chicago Transit Authority trains, locally referred to as "the 'L' ", (after "elevated train") serving Chicago and the near suburbs
- Pace Suburban Bus operates suburban bus and regional vanpool, paratransit, and ride-matching services in the Chicagoland region.
- Metra run by the Northeast Illinois Regional Commuter Railroad Corporation:
- 4 lines serving southern Cook County and Will County
- 3 lines serving western Cook County, DuPage County, and Kane County
- 2 lines serving northern Cook County and Lake County
- 1 line serving northern Cook County, Lake County, and Kenosha County
- 1 line serving northwestern Cook County and McHenry County
- South Shore Line shares the Metra Electric Line in Illinois and connects Chicago to Gary, Michigan City, and ending at South Bend.
- Amtrak operates Union Station which is the major Amtrak passenger rail hub with connections to Metra and the within a few blocks of connections to several 'L' lines. Amtrak also operates a connecting station out of Joliet.
Major highways
[edit]
Interstates
[edit]
- Interstate 41 (I-41) runs concurrently with Interstate 94 from the northern terminus of the Tri-State Tollway to Milwaukee.
- Interstate 55 (I-55) is the Adlai Stevenson Expy.
- I-355 is the Veterans Memorial Tollway (formerly North-South Tollway).
- I-57 is unofficially the "West Leg" of the Dan Ryan Expy.
- I-65 has no name, whether official or unofficial.
- I-80 is officially called the Borman Expy (cosigned with I-94), Kingery Expy (cosigned with I-94 for 3 miles), Tri-State Tollway (cosigned with I-294 for 4 miles) and is unofficially called the Moline Expy west of I-294.
- I-88 is the Ronald Reagan Memorial Tollway (formerly East-West Tollway)
- I-90 is locally known as Jane Addams Tollway (formerly Northwest Tollway), John F. Kennedy Expy (cosigned with I-94), Dan Ryan Expy (cosigned with I-94), and Chicago Skyway Toll Bridge.
- I-94 is Tri-State Tollway in Lake County, Edens Spur, Edens Expy, John F. Kennedy Expy (cosigned with I-90), Dan Ryan Expy (cosigned with I-90), Bishop Ford Frwy (formerly Calumet Expy), Kingery Expy (cosigned with I-80) and Borman Expy (cosigned with I-80).
- I-190 is the John F. Kennedy Expy spur heading into Chicago-O'Hare Int'l Airport.
- I-290 is the Dwight D. Eisenhower Expy.
- I-294 is the Tri-State Tollway.
Other main highways
[edit]
- US Routes in the Illinois part of the area include: US 6, US 12, US 14, US 20, US 30, US 34, US 41, US 45, and US 52.
- Illinois Route 53, an arterial north–south state highway running through Grundy, Will, DuPage, Cook and Lake counties
- Historic US Route 66's eastern terminus is in Chicago.
Major corridors
[edit]
In addition to the Chicago Loop, the metro area is home to a few important subregional corridors of commercial activities. Among them are:
- Illinois Technology and Research Corridor, along the Ronald Reagan Memorial Tollway (Interstate 88)
- Golden Corridor, along the Jane Addams Memorial Tollway (Interstate 90)
- Lakeshore Corridor, along the Edens Expressway and Tri-State Tollway
Culture
[edit]
Sports
[edit]
Main article: Sports in Chicago
Listing of the professional sports teams in the Chicago metropolitan area
Major league professional teams:
- Major League Baseball (MLB)
- Chicago Cubs
- Chicago White Sox
- National Football League (NFL)
- National Basketball Association (NBA)
- National Hockey League (NHL)
- Major League Soccer (MLS)
Other professional teams:
- Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA)
- National Women's Soccer League (NWSL)
- American Association of Professional Baseball (AA)
- Chicago Dogs
- Kane County Cougars
- Gary SouthShore RailCats
- American Hockey League (AHL)
- NBA G League (NBAGL)
- Major League Rugby (MLR)
The Chicagoland Speedway oval track has hosted NASCAR Cup Series and IndyCar Series races. The Chicago Marathon is one of the World Marathon Majors. The Western Open and BMW Championship are PGA Tour tournaments that have been held primarily at golf courses near Chicago.
NCAA Division I College Sports Teams:
- Atlantic 10 Conference
- Loyola University Chicago Ramblers
- Big East Conference
- DePaul University Blue Demons
- Big Ten Conference
- Northwestern University Wildcats (Evanston)
- Mid-American Conference
- Northern Illinois University Huskies (DeKalb)
- Missouri Valley Conference
- University of Illinois Chicago Flames
- Valparaiso University Beacons (Valparaiso, IN)
- Northeast Conference
- Chicago State University Cougars
Cuisine
[edit]
Further information: Chicago § Cuisine
- Chicago-style hot dog
- Chicago-style pizza
- Italian beef
- Caramel popcorn
[edit]
Main article: Media in Chicago
The two main newspapers are the Chicago Tribune and the Chicago Sun-Times. Local television channels broadcasting to the Chicago market include WBBM-TV 2 (CBS), WMAQ-TV 5 (NBC), WLS-TV 7 (ABC), WGN-TV 9 (Ind), WTTW 11 (PBS), MeTV 23, WCIU 26 (CW), WFLD 32 (FOX), WCPX-TV 38 (Ion), WSNS-TV 44 (Telemundo), WPWR-TV 50 (MyNetworkTV), and WJYS-TV 62 (The Way). Radio stations serving the area include: WBBM (AM), WBEZ, WGN (AM), WMBI, WLS (AM), and WSCR.
Education
[edit]
Further information: List of school districts in Illinois, List of school districts in Indiana, and List of colleges and universities in Chicago
 Whitney M. Young Magnet High School in Chicago
Whitney M. Young Magnet High School in Chicago
Elementary and secondary education within the Chicago metropolitan area is provided by dozens of different school districts, of which by far the largest is the Chicago Public Schools with 400,000 students.[42] Numerous private and religious school systems are also found in the region, as well as a growing number of charter schools. Racial inequalities in education in the region remain widespread, often breaking along district boundaries;[43] for instance, educational prospects vary widely for students in the Chicago Public Schools compared to those in some neighboring suburban schools.[44]
Historically, the Chicago metropolitan area has been at the center of a number of national educational movements, from the free-flowing Winnetka Plan to the regimented Taylorism of the Gary Plan.[45] In higher education, University of Chicago founder William Rainey Harper was a leading early advocate of the junior college movement; Joliet Junior College is the nation's oldest continuously operating junior college today.[46] Later U of C president Robert Maynard Hutchins was central to the Great Books movement, and programs of dialogic education arising from that legacy can be found today at the U of C, at Shimer College,[47] and in the City Colleges of Chicago and Oakton College in the Northwest suburbs.[48]
Area codes
[edit]
Main article: List of Illinois area codes
From 1947 until 1988, the Illinois portion of the Chicago metro area was served by a single area code, 312, which abutted the 815 area code. In 1988 the 708 area code was introduced and the 312 area code became exclusive to the city of Chicago.
It became common to call suburbanites "708'ers", in reference to their area code.
The 708 area code was partitioned in 1996 into three area codes, serving different portions of the metro area: 630, 708, and 847.
At the same time that the 708 area code was running out of phone numbers, the 312 area code in Chicago was also exhausting its supply of available numbers. As a result, the city of Chicago was divided into two area codes, 312 and 773. Rather than divide the city by a north–south area code, the central business district retained the 312 area code, while the remainder of the city took the new 773 code.
In 2002, the 847 area code was supplemented with the overlay area code 224. In February 2007, the 815 area code (serving outlying portions of the metro area) was supplemented with the overlay area code 779. In October 2007, the overlay area code 331 was implemented to supplement the 630 area with additional numbers.
Plans are in place for overlay codes in the 708, 773, and 312 regions as those area codes become exhausted in the future.
- 312 Chicago - City (The Loop and central neighborhoods, e.g. the Near North Side)
- 773 Chicago - City (Everywhere else within the city limits, excluding central area)
- 872 Chicago - City (overlay for 312 & 773, effective November 7, 2009)
- 847/224 (North and Northwest Suburbs)
- 630/331 (Outer Western Suburbs)
- 708 (South and Near West Suburbs)
- 815/779 (Rockford & Joliet: Far Northwest/Southwest Suburbs)
- 219 (Northwest Indiana)
- 574 (North-central Indiana)
- 262 (Southeast Wisconsin surrounding Milwaukee County)
Proposed overlays
[edit]
- 464 overlay for 708 (January 21, 2022, rollout)
See also
[edit]
- Index of Illinois-related articles
References
[edit]
- ^ a b
"Elevations of the 50 Largest Cities". U.S. Geological Survey. Archived from the original on November 9, 2013. Retrieved January 23, 2016.
Chicago city proper only
- ^ "2020 Population and Housing State Data". United States Census Bureau, Population Division. August 12, 2021. Retrieved November 19, 2021.
- ^ "USA: Combined Metropolitan Areas". CityPopulation.de. August 2021. Retrieved November 19, 2021.
- ^ "Total Gross Domestic Product for Chicago-Naperville-Elgin, IL-IN-WI (MSA)". Federal Reserve Economic Data. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Combined Statistical Areas in the United States and Puerto Rico: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2019 (CSA-EST2019-ANNRES)". United States Census Bureau, Population Division. March 2020. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Metropolitan Statistical Areas in the United States and Puerto Rico: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2019 (CBSA-MET-EST2019-ANNRES)". United States Census Bureau, Population Division. March 2020. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- ^ "CAEMP25N Total Full-Time and Part-Time Employment by NAICS Industry 1/ 2018". Bureau of Economic Analysis. November 14, 2019. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- ^ "CAGDP1 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) summary by county and metropolitan area 2018". Bureau of Economic Analysis. December 12, 2019. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- ^ "Economy". Worldbusinesschicago.com. Retrieved October 3, 2017.
- ^ "Chicago Named Nation's Top Metro Area for Corporate Relocation For the Sixth Straight Year". World Business Chicago. March 25, 2019. Retrieved July 21, 2019.
- ^ a b c "Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas Population Totals and Components of Change: 2020-2021". Census.gov. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 12, 2023.
- ^ "The World's Cities in 2018" (PDF). United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- ^ As defined by Construction Data Company.
- ^ a b Fuller, Jack (2005). "Chicagoland". The Electronic Encyclopedia of Chicago. Chicago Historical Society. Retrieved February 20, 2010.
- ^ "The Press: The Colonel's Century". TIME. June 9, 1947. Archived from the original on September 18, 2008. Retrieved February 20, 2010.
- ^ O'Donnell Bennett, James (July 27, 1926). "Chicagoland's Shrines: A Tour of Discoveries". Chicago Daily Tribune (1923-1963). Archived from the original on September 10, 2010. Retrieved February 20, 2010.
- ^ Cronon (1992); Keating (2005); Keating (2004)
- ^ "Classifieds map of Chicagoland". Chicagotribune.com. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- ^ [1] Archived November 10, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "About Chicagoland". Chicagoland Chamber of Commerce. Archived from the original on October 29, 2013. Retrieved October 25, 2013.
- ^ "Bidtool Coverage area: Chicago, Indiana, Wisconsin, Colorado, Kentucky project leads". Bidtool.net. Archived from the original on July 15, 2011. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- ^ Mariner, Richard D. (July 10, 2018). "Collar Counties". The Electrictronic Encyclopedia of Chicago. Chicago, IL: Chicago Historical Society (2005), Newberry Library (2004).
- ^ "Chicago Metropolitan Agency for Planning". Chicagoareaplanning.org. Archived from the original on August 12, 2006. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- ^ "About - CMAP". Cmap.illinois.gov. Retrieved September 7, 2015.
- ^ Nowak, David J.; Hoehn, Robert E. III; Bodine, Allison R.; Crane, Daniel E.; Dwyer, John F.; Bonnewell, Veta; Watson, Gary. (September 17, 2013). "Urban trees and forests of the Chicago region". Nrs.fs.fed.us. doi:10.2737/NRS-RB-84. Retrieved September 7, 2015.
- ^ "Regional Tree Census | The Morton Arboretum". Mortonarb.org. Archived from the original on May 15, 2015. Retrieved September 7, 2015.
- ^ "Grid View: Table B03002 - Census Reporter". censusreporter.org. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- ^ "Grid View: Table B04006 - Census Reporter". censusreporter.org. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- ^ "Grid View: Table B02018 - Census Reporter". censusreporter.org. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- ^ "Grid View: Table B03001 - Census Reporter". censusreporter.org. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- ^ "Grid View: Table B02009 - Census Reporter". censusreporter.org. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- ^ "Kendall County is fastest growing in the nation". Daily Herald. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- ^ "Census profile: Chicago-Naperville-Elgin, IL-IN-WI Metro Area". Census Reporter. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- ^ "Historical Metropolitan Area Definitions". Census.gov. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- ^ "List of 2020 Census Urban Areas". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 7, 2023.
- ^ Carl Sandburg. "Chicago". Poetry: A Magazine of Verse, vol. 3, no. 6 (March 1914):191-192.
- ^ RON STARNER. "TOP METROS OF 2007 - Site Selection magazine, March 2008". Siteselection.com. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- ^ RON STARNER (March 9, 2009). "TOP METROS OF 2008 - Site Selection magazine, March 2009". Siteselection.com. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- ^ "TOP METROS OF 2009 - Site Selection Magazine, March 2010". Siteselection.com. Archived from the original on July 2, 2011. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- ^ Brat, Ilan (November 8, 2006). "Tale of a Warehouse Shows How Chicago Weathers a Decline". The Wall Street Journal. p. A1. Retrieved February 20, 2010.
- ^ "Chicago Highlighted as the US Railroad Capital by Trains Magazine". WTTW. February 23, 2017. Retrieved March 23, 2019.
- ^ "About CPS". Chicago Public Schools. Retrieved January 26, 2015.
- ^ Moore, Natalie (November 12, 2014). "Why so few white kids land in CPS — and why it matters". WBEZ. Archived from the original on January 17, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2015.
- ^ Bogira, Steve (October 17, 2012). "Two students, two high schools, two divergent paths to college". Chicago Reader.
- ^ Thiede, Robert. "Gary Plan". Britannica.com. Retrieved January 16, 2015.
- ^ Sydow, Debbie; Alfred, Richard (2012). Re-visioning Community Colleges: Positioning for Innovation. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 13. ISBN 978-1442214880.
- ^ Ronson, Jon (December 6, 2014). "Shimer College: The Worst School in America?". The Guardian.
- ^ "Great Books program". Oakton Community College. Retrieved January 26, 2015.
Further reading
[edit]
- Fischer, Paul B. (July 28, 1993). Racial and Locational Patterns of Subsidized Housing in the Chicago Suburbs: A Report to the MacArthur Foundation (Archive). Lake Forest, Ill.: Lake Forest College. Report to the MacArthur Foundation.
- Lewinnek, Elaine (2014). The Working Man's Reward: Chicago's Early Suburbs and the Roots of American Sprawl. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
External links
[edit]
Chicago metropolitan area at Wikipedia's sister projects
 Definitions from Wiktionary
Definitions from Wiktionary Media from Commons
Media from Commons Travel information from Wikivoyage
Travel information from Wikivoyage Data from Wikidata
Data from Wikidata
- Encyclopedia of Chicago (2004), comprehensive coverage of city and suburbs, past and present
- U.S. Census Urbanized Area Outline Map (2000)
- Chicago-Naperville-Michigan City, IL-IN-WI Combined Statistical Area (2012) map
- Illinois CBSAs and Counties (2013) map
- U.S. Census Bureau Chicago city, Illinois QuickFacts
- Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas
- About Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas
- History of Metropolitan Areas
- Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas Population Totals and Components of Change: 2010–2019
Chicago metropolitan area
| |
| Major city |
|
|
Cities
(over 30,000 in 2020) |
- Aurora
- Berwyn
- Calumet City
- Crown Point
- Crystal Lake
- DeKalb
- Des Plaines
- Elgin
- Elmhurst
- Evanston
- Gary
- Hammond
- Highland Park
- Joliet
- Kenosha
- Naperville
- North Chicago
- Park Ridge
- Portage
- St. Charles
- Valparaiso
- Waukegan
- Wheaton
|
Towns and villages
(over 30,000 in 2020) |
- Addison
- Arlington Heights
- Bartlett
- Bolingbrook
- Buffalo Grove
- Carol Stream
- Carpentersville
- Cicero
- Downers Grove
- Elk Grove Village
- Glendale Heights
- Glenview
- Grayslake
- Gurnee
- Hanover Park
- Hoffman Estates
- Lombard
- Merrillville
- Mount Prospect
- Mundelein
- Niles
- Northbrook
- Oak Lawn
- Oak Park
- Orland Park
- Oswego
- Palatine
- Plainfield
- Romeoville
- Schaumburg
- Skokie
- Streamwood
- Tinley Park
- Wheeling
- Wonder Lake
- Woodridge
|
| Counties |
- Cook
- DeKalb
- DuPage
- Grundy
- Jasper
- Kane
- Kankakee
- Kendall
- Kenosha
- Lake, IL
- Lake, IN
- McHenry
- Newton
- Porter
- Will
|
| Regions |
- Great Lakes
- Northern Illinois
- Northern Indiana
|
| Sub-regions |
- Chicago Southland
- Eastern Ridges and Lowlands
- Fox Valley (Illinois)
- Golden Corridor
- Illinois Technology and Research Corridor
- North Shore (Chicago)
- Northwest Indiana
|
|
Illinois, United States
|
World's 50 most-populous urban areas
| |
| |
- Tokyo
- Jakarta
- Delhi
- Guangzhou–Foshan
- Mumbai
- Manila
- Shanghai
- Seoul
- Cairo
- Mexico City
|
- Kolkata
- São Paulo
- New York
- Karachi
- Dhaka
- Bangkok
- Beijing
- Moscow
- Shenzhen
- Buenos Aires
|
- Los Angeles
- Johannesburg-Pretoria
- Bengaluru
- Chengdu
- Ho Chi Minh City
- Osaka–Kobe–Kyoto
- Lagos
- Istanbul
- Lahore
- Kinshasa–Brazzaville
|
- Tehran
- Chongqing
- Rio de Janeiro
- Xi'an
- Chennai
- Paris
- Zhengzhou
- Luanda
- London
- Dongguan
|
- Lima
- Wuhan
- Bogotá
- Tianjin
- Hyderabad
- Taipei
- Hangzhou
- Nagoya
- Surabaya
- Bandung
|
|
Great Lakes megalopolis as defined by the RPA
| |
|
Includes all metropolitan areas that have a population of 150,000 or greater according to the most recent national census.
|
| Great Lakes region cities |
- Brantford
- Buffalo–Niagara Falls
- Chicago
- Cleveland
- Detroit
- Duluth–Superior
- Erie
- Grand Rapids
- Guelph
- Green Bay
- Hamilton
- Holland
- Kalamazoo
- Kenosha
- Lansing
- London
- Milwaukee
- Muskegon
- Niagara Region
- St. Catharines
- Niagara Falls
- Welland
- Niles
- Oshawa
- Rochester, New York
- South Bend
- Thunder Bay
- Toledo
- Toronto
- Traverse City
- Waterloo Region
- Kitchener
- Cambridge
- Waterloo
- Windsor
|
|
| Surrounding cities |
- Akron
- Altoona
- Ann Arbor
- Barrie
- Bloomington, Indiana
- Bloomington–Normal
- Bloomington, Illinois
- Normal
- Canton
- Champaign
- Cincinnati
- Columbus
- Dayton
- Eau Claire
- Elkhart
- Evansville
- Fargo
- Flint
- Fort Wayne
- Fox Cities
- Indianapolis
- Jackson
- Janesville–Beloit
- Kankakee
- Kingston
- La Crosse–Onalaska
- Lafayette
- Madison
- Mahoning Valley
- Minneapolis–Saint Paul
- Greater Montreal
- National Capital Region
- Pittsburgh
- Peoria
- Peterborough
- Rockford
- Rochester, Minnesota
- Saguenay
- St. Cloud
- Saginaw
- Sioux Falls
- Springfield
- Sudbury
- Syracuse
- Terre Haute
- Trois-Rivières
- Utica–Rome
- Quad Cities
- Bettendorf
- Davenport
- East Moline
- Moline
- Rock Island
- Greater Quebec
|
| Cities of states south of region |
- Elizabethtown
- Kansas City
- Louisville
- St. Louis
- Topeka
- Wheeling
|
| Other metro-regions |
- Quebec City–Windsor Corridor
- Golden Horseshoe
- Greater Toronto and Hamilton Area
- Detroit–Windsor
- Greater Pittsburgh
- Metro East
|
|
Other megaregions
|
Authority control databases  |
| International |
|
| National |
- Germany
- United States
- Israel
|