Introduction
IP addresses play a crucial role in connecting devices to the internet. They serve as unique identifiers for devices, allowing them to communicate with each other and access online resources. When it comes to IP addresses, there are two main types: static and dynamic. In this blog post, we will delve into the differences between these two types and explore their advantages and disadvantages.
Static IP Addresses
A static IP address is a fixed address that remains constant for a device. It is manually assigned to a device by a network administrator or an Internet Service Provider (ISP). Static IP addresses are typically used for devices that require a permanent and consistent connection, such as servers, printers, or routers.
Advantages of Static IP Addresses
1. Reliable Connectivity: Static IP addresses provide a stable and uninterrupted connection, as the address remains the same over time.
2. Hosting Services: Static IP addresses are essential for hosting websites, email servers, or any other online services that require a consistent address for users to access.
3. Remote Access: With a static IP address, it is easier to remotely access devices or networks securely.
Disadvantages of Static IP Addresses
1. Configuration Complexity: Setting up a static IP address requires manual configuration, which can be complex for non-technical users.
2. Limited Availability: Static IP addresses are limited in number and may not be readily available from ISPs.
3. Higher Costs: Some ISPs charge additional fees for static IP addresses, making them more expensive compared to dynamic IP addresses.
Dynamic IP Addresses
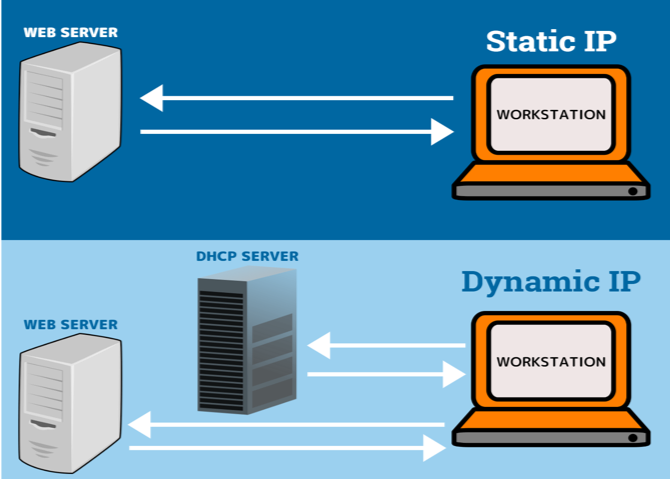
A dynamic IP address is an address that is automatically assigned to a device by a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server. These addresses are temporary and can change each time a device connects to the network or after a certain period of time.
Advantages of Dynamic IP Addresses
1. Easy Configuration: Dynamic IP addresses are automatically assigned, eliminating the need for manual configuration.
2. Cost-Effective: Dynamic IP addresses are generally provided by ISPs at no additional cost.
3. Enhanced Security: Dynamic IP addresses offer a level.
Summary
IP addresses can be classified into two categories: static and dynamic. A static IP address is manually assigned to a device and remains constant over time. It provides a fixed location for the device on the internet, making it easier to manage and access remotely. On the other hand, dynamic IP addresses are automatically assigned by a DHCP server and can change periodically. This type of address is commonly used in home networks and allows for efficient utilization of available IP addresses.
Static IP addresses offer benefits such as consistent accessibility, better security, and easier hosting of services. They are ideal for devices that require a permanent online presence, such as servers or network printers. However, they can be more expensive and require manual configuration.
Dynamic IP addresses, on the other hand, are more flexible and cost-effective. They are commonly used by internet service providers (ISPs) to efficiently allocate IP addresses to their customers. Dynamic addressing allows for better utilization of available IP addresses, as they can be reused when not in use. However, it can pose challenges for remote access and hosting services that require a fixed IP address.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between static and dynamic IP addresses is essential for managing and optimizing network connectivity. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the devices and network infrastructure. By considering factors such as cost, acce check my reference ssibility, and security, organizations and individuals can make informed decisions regarding the type of IP address that best suits their needs.
- Q: What is an IP address?
- A: An IP address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.
- Q: What is a static IP address?
- A: A static IP address is a fixed address that is manually assigned to a device and remains constant, allowing it to be easily identified on a network.
- Q: What is a dynamic IP address?
- A: A dynamic IP address is an address that is automatically assigned to a device by a network’s Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server. It can change periodically.
- Q: What are the advantages of a static IP address?
- A: Static IP addresses provide stability, as they do not change. They are useful for hosting websites, running servers, or accessing devices remotely.
- Q: What are the advantages of a dynamic IP address?
- A: Dynamic IP addresses are more cost-effective and easier to manage. They are suitable for most home users and small businesses that do not require constant access to specific devices.
- Q: Can I switch between static and dynamic IP addresses?
- A: Yes, you can switch between static and dynamic IP addresses. However, it usually requires contacting your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to make the necessary changes.
- Q: How do I find my IP address?
- A: You can find your IP address by using online IP lookup tools, checking your network settings, or typing “ipconfig” in the command prompt (Windows) or “ifconfig” in the terminal (Mac/Linux).
- Q: Are IP addresses permanent?
- A: IP addresses can be permanent (static) or temporary (dynamic). Static IP addresses remain the same unless manually changed, while dynamic IP addresses can change over time.

Welcome to my website! My name is Levi McBryde, and I am a dedicated professional Hardware Upgrade Technician with a passion for Network Solutions, Hardware Upgrades, Augmented Reality, and Game Development. With years of experience in the field, I am committed to providing top-notch services and solutions to meet your technological needs.
