
How to Ensure Compliance with Codes and Standards During PWHT Operations
Ensuring compliance with codes and standards during Post Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT) operations is quite the task, ain't it? It's not just about following a set of instructions; rather, it’s about understanding the why's and how's that govern these crucial procedures. Firstly, one must get their hands on the relevant documents. You know - those codes and standards that seem to always be updating just when you think you've got a handle on them! It's essential to stay current with organizations like ASME or API since they're constantly revising their guidelines. Oh, don't forget local regulations; they can be pretty strict too! Now, getting your team on board is another story. Training – that's what it all boils down to (and let's face it; nobody really enjoys those long training sessions). But hey, if workers aren’t familiar with the specs, how could they possibly ensure compliance? So we squeeze in those educational nuggets whenever possible – even though some might think "Here we go again..." But remember! Training isn't a one-off event; refresher courses are a must. Documentation – oh boy, does this part matter! If it wasn’t documented, did

What is it? Why is PWHT needed? How is PWHT done?
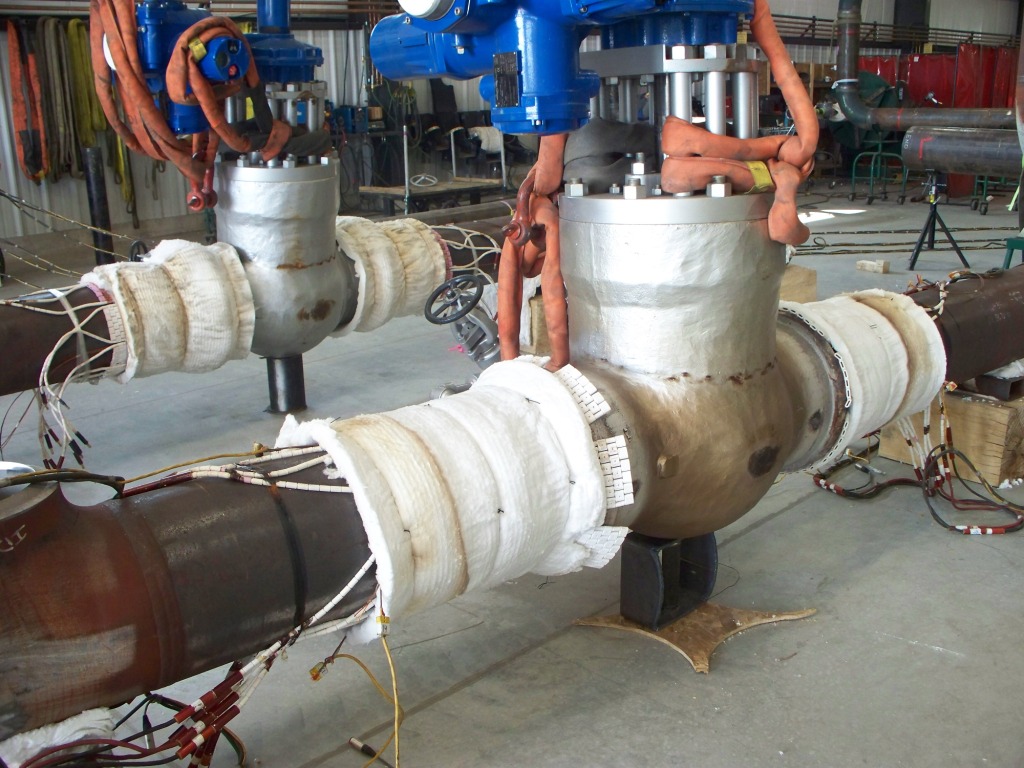
Post-weld heat treatment (pwht) is a procedure designed to enhance the mechanical strength and toughness of the weld. It also reduces the amount of tensile welding residual stresses. The procedure requires a number of precautions. One important consideration is the type of equipment used for the process. An automatic temperature recorder is required to ensure proper calibration. Calibration should be done at least once a year. A potentiometer is also necessary to control the level of power applied to the coils. A post-heating process is necessary to prevent hydrogen from causing cold cracking on the surface of the weld. The need for the pwht is driven by either fabrication code or by service environment concerns. The requirement and specification of pwht operation is governed by the objectives as stated bellow, not all the pwht operations are same. As specified by fabrication code, which generally aimed at tempering and relaxation of residual stress, so as to reduce the susceptibility to brittle failure, and is triggered by material type and thickness. As needed for service requirements, which commonly aimed at reduction of hardness and stress relaxation. The following information is gathered from aws a 10. 10, it condenses the

Need help or have a question?
Do you have any questions or would you like to request a quote without obligation? please contact us. "the complete guide to post weld heat treatment pwht: standards, procedures, applications, and interview q&a" is an essential resource for engineers, welders, inspectors, and technicians involved in post-weld heat treatment (pwht). This pwht book covers everything you need to know about pwht, including the historical background, purpose and benefits, materials and welding methods that require pwht, pwht methods, temperature and time requirements, cooling methods, process control and monitoring, applications, effects of pwht, standards and codes related to pwht, quality control and assurance, pwht interview questions and answers, health and safety, and future directions in pwht. This weld heat treatment guidebook provides detailed information on the different types of materials that require pwht, welding methods, and defects that pwht can mitigate. What is Post Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT)? Localized pwht with ceramic mat heaters ceramic mat heaters are used for localized post weld heat treatment to provide a controlled and consistent heat source for specific areas of a welded joint. These heaters are typically made from high-temperature ceramic materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and provide a uniform heat distribution.
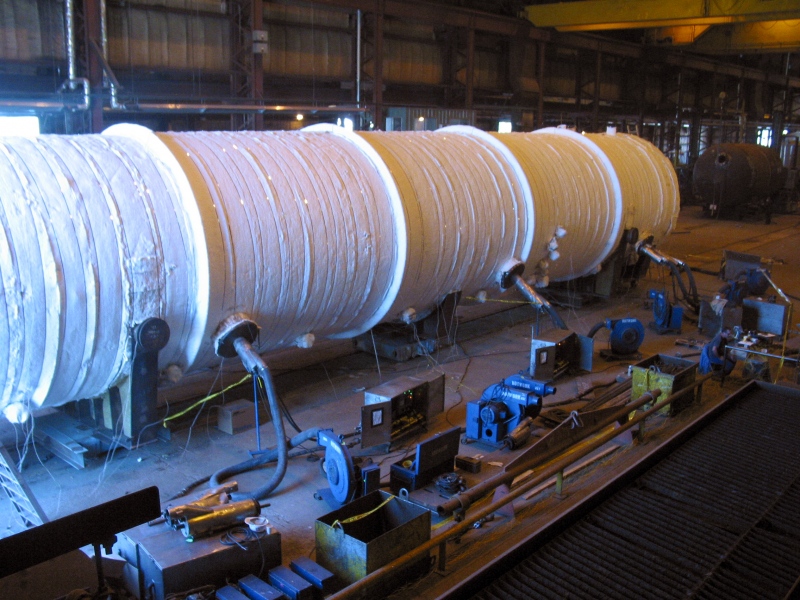
Recent Studies on PWHT
Pwht of carbon steels pwht of stainless steels and nickel alloys pwht of heat-treatable alloys pwht of exotic materials and superalloys case studies on material-specific pwht. Post Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT) Post weld heat treatment is a post welding heating process used to improve the properties of the weldment. Heat treatment following welding may be carried out for one or more of three fundamental reasons (1): to achieve dimensional stability in order to maintain tolerances during machining operations or during shake-down in service to produce specific metallurgical structures in order to achieve the required mechanical properties to reduce the risk of in-service problems such as stress corrosion or brittle fracture by reducing the residual stress in the welded component the need for pwht is normally driven by code requirements. For section i these requirements can be found in section pw-39 requirements for postweld heat treatment. Post weld heat treatment (pwht) is a thermal process that is performed on welded materials after welding to reduce residual stresses and improve the welded joint’s mechanical properties. Residual stresses occur during welding due to heat input, leading to flaws such as distortion, cracking, and defects in the welded joint. Pwht relieves these stresses and enhances the joint’s

Post weld heat treatment
Controlled process of reheating materials post weld heat treatment (pwht) is a controlled process in which a material that has been welded is reheated to a temperature below its lower critical transformation temperature, and then it is held at that temperature for a specified amount of time. It is often referred to as being any heat treatment performed after welding; however, within the oil, gas, petrochemical and nuclear industries, it has a specific meaning. Industry codes, such as the asme pressure vessel and piping codes, often require mandatory performance of pwht on certain materials to ensure a safe design with optimal mechanical and metallurgical properties. By samudrapom dam aug 10 2022 this article discusses the post weld heat treatment (pwht) process and its effectiveness in reducing the residual stresses and improving the mechanical properties of weldments. Image credit: funtay/shutterstock. Com. Comment 5 | share | tweet | share | pin it | print | email have you heard of post weld heat treatment (pwht)? of course you have. If you are involved in welding you have definitely heard this term. But what is phwt? when is pwht required? what temperature should pwht be done at? heat treating of materials can be a