what drug rehab centers accept medicaid
A person who relapses will start using drugs again, even though they tried to stop. A relapse is a sign that more therapy or a different kind of therapy is needed.
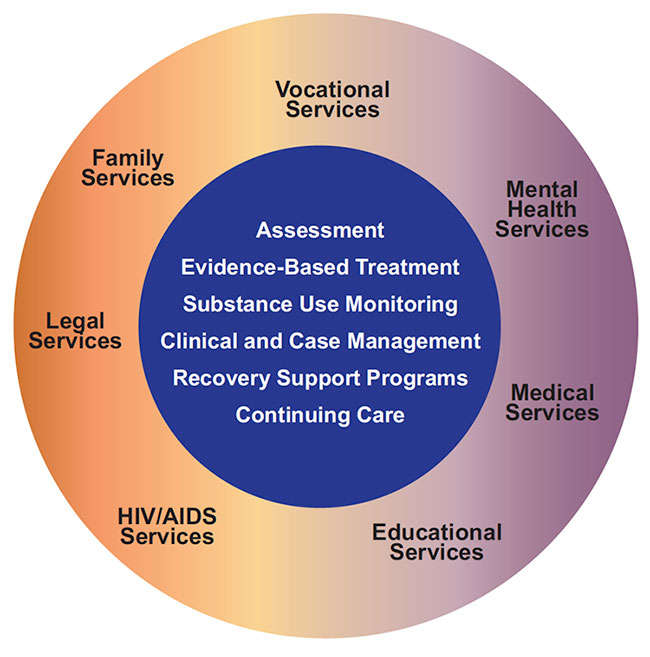
Important points to be aware Drug addiction, a chronic disorder, is defined as compulsive drug search and use. While it is not easy to control its negative consequences, it is often a permanent condition.
.jpg)