Introduction
Teeth grinding, also known as bruxism, is a common dental condition that affects many individuals. It involves the involuntary clenching, gnashing, or grinding of teeth, often during sleep. While occasional teeth grinding may not cause significant harm, chronic and untreated bruxism can lead to various long-term effects on oral health and overall well-being.
1. Dental Damage
One of the primary long-term effects of untreated teeth grinding is dental damage. The constant grinding and clenching exert excessive force on the teeth, leading to wear and tear. Over time, this can result in chipped, cracked, or fractured teeth. Additionally, bruxism can wear down the enamel, making the teeth more susceptible to decay and sensitivity.
2. Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMJ)
Untreated teeth grinding can also contribute to the development of temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ). The excessive pressure exerted on the jaw joint during grinding can cause inflammation and damage to the joint. This can lead to symptoms such as jaw pain, headaches, difficulty in opening or closing the mouth, and clicking or popping sounds when chewing or speaking.
3. Gum Recession
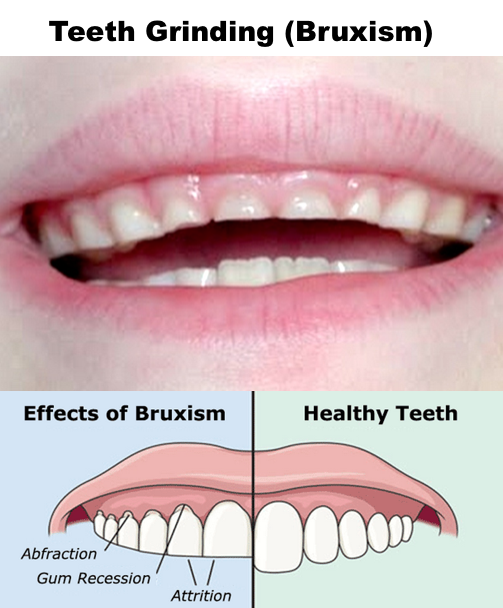
Bruxism can result in gum recession, where the gum tissue gradually pulls away from the teeth, exposing the roots. The constant grinding motion can irritate and damage the gums, leading to their recession. Gum recession not only affects the aesthetics of the smile but also increases the risk of tooth sensitivity, root decay, and tooth loss.
4. Tooth Sensitivity
Individuals with untreated teeth grinding often experience tooth sensitivity. The wearing down of the enamel exposes the underlying dentin, which contains microscopic tubules that connect to the nerves of the teeth. This exposure to external stimuli, such as hot or cold foods and beverages, can cause discomfort and pain.
5. Sleep Disorders
Teeth grinding can disrupt sleep patterns, both for the individual grinding their teeth and their sleep partner. The grinding noises can be loud and disturbing, leading to sleep disturbances and even sleep disorders such as insomnia. The lack of quality sleep can have.
Summary
Untreated teeth grinding can have serious long-term effects on oral health. The constant grinding and clenching of teeth can lead to tooth damage, such as fractures, chips, and wear. It can also cause jaw pain, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, and headaches. Additionally, untreated bruxism can result in gum recession, tooth sensitivity, and even tooth loss. It is crucial to address teeth grinding early on to prevent these complications. Seeking prof additional info essional dental care and using protective measures, such as mouthguards, can help manage and alleviate the long-term effects of untreated bruxism.
- Q: What are the long-term effects of untreated teeth grinding?
- A: Untreated teeth grinding, also known as bruxism, can lead to various long-term effects including:
- – Worn down tooth enamel
- – Cracked or chipped teeth
- – Tooth sensitivity
- – Jaw pain and temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ)
- – Headaches and migraines
- – Sleep disturbances
- – Facial muscle hypertrophy (enlargement)
- – Changes in bite alignment
- – Increased risk of tooth decay and gum disease
- – Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- – Sleep apnea

Welcome to my website! My name is Jonathan Northcote, and I am a dedicated and experienced Dental Technician specializing in Dental Beautification, Wisdom Tooth Extraction, and Teeth Grinding Solutions. With a passion for creating beautiful smiles and improving oral health, I am committed to providing exceptional dental care and solutions to my patients.