Periodontal Disease: Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Imagine you’re walking through a beautiful garden, appreciating the vibrant colors and fragrant flowers. But as you get closer, you notice something amiss wilted petals, yellowing leaves, and a sense of decay lingering in the air.
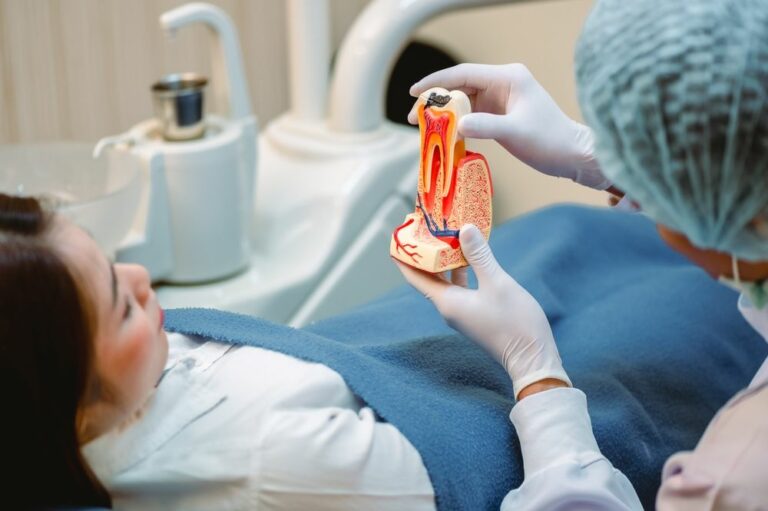
Just like this garden, your oral health can also fall victim to the ravages of periodontal disease. With millions of people affected by this condition, it’s crucial to understand the risk factors and prevention strategies that can help you maintain a healthy smile.
So, what are the key factors that contribute to periodontal disease, and how can you protect yourself? Let’s explore.
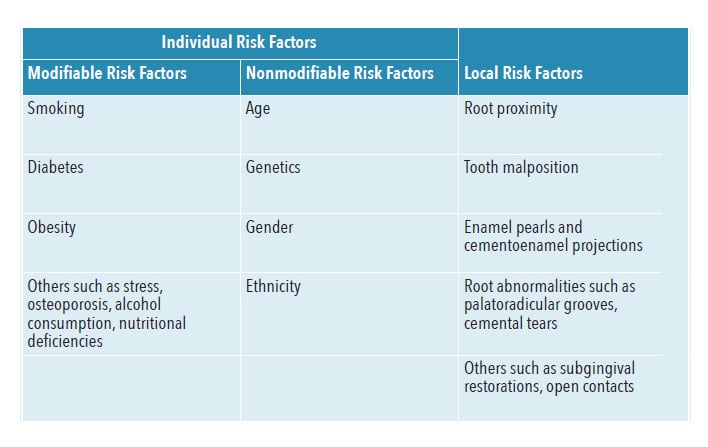
Common Risk Factors
To effectively prevent periodontal disease, it’s important to be aware of the common risk factors that can contribute to its development.
One of the most significant risk factors is poor oral hygiene. When you don’t brush and floss regularly, plaque builds up on your teeth and gums, leading to inflammation and eventually periodontal disease.
Another common risk factor is tobacco use. Smoking or chewing tobacco not only stains your teeth and causes bad breath, but it also weakens your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infection and heal gum tissue.
Additionally, certain medical conditions can increase your risk of developing periodontal disease. Conditions like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and cancer weaken the immune system and make you more susceptible to gum infections.
Furthermore, hormonal changes in women, such as those during pregnancy or menopause, can also increase the risk of gum disease.
Lastly, a family history of periodontal disease can make you more prone to developing the condition yourself.
Poor Oral Hygiene Habits
Improper brushing and flossing techniques can contribute to the development of periodontal disease. When you don’t brush your teeth properly, plaque can build up, leading to gum inflammation and eventually periodontal disease. It’s important to use the correct technique when brushing your teeth. Start by placing your toothbrush at a 45-degree angle against your gumline and gently brush using short back-and-forth motions. Be sure to brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces. Don’t forget to brush your tongue as well to remove bacteria and freshen your breath.
Flossing is another crucial step in maintaining good oral hygiene. When you don’t floss regularly or use the wrong technique, plaque and food particles can remain trapped between your teeth, increasing the risk of gum disease. To floss effectively, take about 18 inches of floss and wrap it around your middle fingers, leaving about 1-2 inches of floss between your hands. Gently insert the floss between your teeth, making a C shape around each tooth. Move the floss up and down to remove plaque and debris.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
If you smoke or use tobacco products, your risk of developing periodontal disease significantly increases. Research has shown that smoking and tobacco use are major risk factors for gum disease. Smoking weakens your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infections, including those that affect your gums. It also reduces blood flow to the gums, which impairs their ability to heal and leads to a slower recovery from periodontal treatment. Additionally, smoking and tobacco use can mask the signs of gum disease, making it harder to detect and treat in its early stages.
Tobacco products, such as cigarettes and chewing tobacco, contain harmful chemicals that can damage your gums and other oral tissues. These chemicals can cause inflammation, which is a key factor in the development and progression of periodontal disease. Furthermore, smoking and tobacco use can worsen existing gum disease and increase the risk of tooth loss.
If you’re a smoker or use tobacco products, quitting is crucial for maintaining good oral health. Quitting smoking not only reduces your risk of periodontal disease but also improves your overall health. Talk to your healthcare provider about strategies and resources to help you quit smoking. Taking this step won’t only benefit your oral health but also your general well-being.
Diabetes and Chronic Health Conditions
If you have diabetes or other chronic health conditions, you may be at an increased risk for developing periodontal disease. This is because these conditions can weaken your immune system and make it harder for your body to fight off infections, including those that affect your gums and teeth.
Here are three important things to keep in mind:
1. Control your blood sugar levels: High blood sugar levels can contribute to the growth of harmful bacteria in your mouth, increasing your risk of periodontal disease. It’s crucial to manage your diabetes through medication, diet, and exercise to keep your blood sugar levels under control.
2. Practice good oral hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing are essential for preventing periodontal disease. Make sure to brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily. Additionally, using an antiseptic mouthwash can help kill bacteria and reduce plaque buildup.
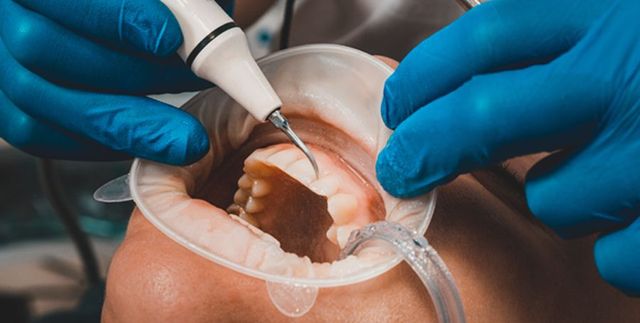
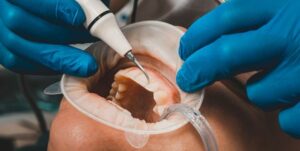
3. Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups are crucial for detecting and treating periodontal disease early on. Your dentist can assess the health of your gums and teeth, provide professional cleanings, and offer personalized advice on oral hygiene practices.
Hormonal Changes and Pregnancy
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can increase the risk of developing periodontal disease. These hormonal fluctuations can have a significant impact on your oral health. The surge in hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, can affect the way your body responds to plaque bacteria. This can lead to an increased risk of gum inflammation and infection.
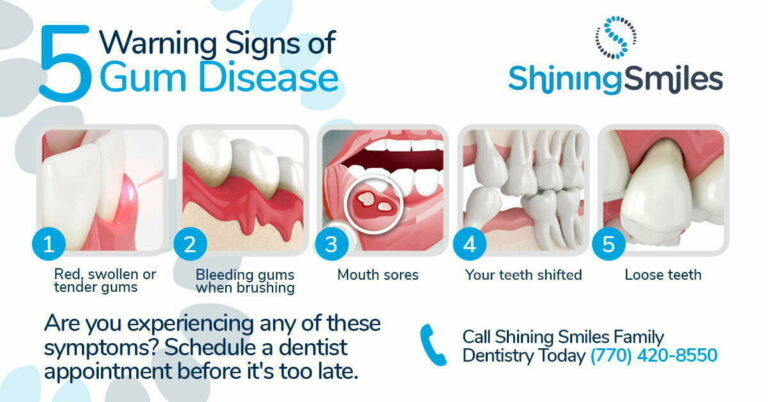
One common condition that pregnant women may experience is called pregnancy gingivitis. This is characterized by swollen, tender, and bleeding gums. Hormonal changes can make your gums more sensitive to the bacteria in plaque, causing them to become inflamed and bleed easily. If left untreated, pregnancy gingivitis can progress to a more severe form of gum disease called periodontitis.
It is important to maintain good oral hygiene during pregnancy to reduce the risk of developing periodontal disease. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, as well as flossing daily. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also crucial to monitor your oral health and address any potential issues.
In addition to practicing good oral hygiene, it’s recommended to eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support your oral health. Avoiding sugary snacks and drinks can help prevent plaque buildup and reduce the risk of gum disease.
Prevention Strategies
To prevent periodontal disease, it’s important to implement effective prevention strategies. Taking care of your oral health is essential in keeping your gums and teeth healthy. Here are three key strategies you can incorporate into your daily routine:
1. Practice good oral hygiene:
– Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste.
– Don’t forget to clean between your teeth using dental floss or interdental brushes.
– Regularly visit your dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups to ensure any potential dental issues are addressed early.
2. Maintain a healthy lifestyle:
– A balanced diet plays a crucial role in preventing periodontal disease.
– Limit sugary and acidic foods and beverages, as they can contribute to tooth decay and gum inflammation.
– Quit smoking or using tobacco products, as they increase the risk of gum disease and hinder the healing process.
3. Manage stress:
– Chronic stress can weaken your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infections, including gum disease.
– Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Periodontal Disease Be Caused by Genetics or Family History?
Yes, periodontal disease can be caused by genetics or family history. Certain genetic factors can make individuals more susceptible to developing periodontal disease. If your family has a history of gum disease, you may be at a higher risk as well.
It’s important to be aware of this risk factor and take proper preventive measures, such as regular dental check-ups and practicing good oral hygiene, to minimize the chances of developing periodontal disease.
Are There Any Specific Medications That Can Increase the Risk of Developing Periodontal Disease?
Yes, there are specific medications that can increase your risk of developing periodontal disease.
Certain medications, such as oral contraceptives, antidepressants, and immunosuppressants, can affect your oral health and make you more susceptible to gum disease.
It’s important to inform your dentist about any medications you’re taking so they can provide appropriate preventive care and closely monitor your oral health.
Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene habits are crucial in managing and preventing periodontal disease.
Can Stress or a Weakened Immune System Contribute to the Development of Periodontal Disease?
Yes, stress and a weakened immune system can contribute to the development of periodontal disease.
When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones that can affect your immune system’s ability to fight off infection. This can make you more susceptible to gum disease.
Additionally, a weakened immune system can also make it harder for your body to fight off the bacteria that cause periodontal disease.
It’s important to manage stress and maintain a healthy immune system to prevent the development of periodontal disease.
Are There Any Specific Dietary Factors That Can Increase the Risk of Periodontal Disease?
There are specific dietary factors that can increase your risk of developing periodontal disease. Certain foods, such as sugary snacks and beverages, can promote the growth of harmful bacteria in your mouth.
Additionally, a diet high in processed foods and low in nutrients can weaken your immune system, making it more difficult for your body to fight off infections.
It’s important to maintain a balanced diet and limit your intake of sugary and processed foods to help prevent periodontal disease.
Can Poor Dental Care During Childhood Increase the Risk of Developing Periodontal Disease Later in Life?
Poor dental care during childhood can increase your risk of developing periodontal disease later in life.
Neglecting to brush and floss regularly, not visiting the dentist for check-ups, and consuming sugary foods can all contribute to the accumulation of plaque and tartar on your teeth.
Over time, this can lead to gum inflammation, gum recession, and eventually periodontal disease.
Taking proper care of your teeth from a young age is essential for maintaining good oral health in the long run.
Conclusion
So, now you know the common risk factors for periodontal disease, such as:
– Poor oral hygiene
– Smoking
– Diabetes
– Hormonal changes during pregnancy
To prevent this condition, it’s important to:
– Maintain good oral hygiene habits
– Quit smoking
– Manage chronic health conditions
– Seek proper dental care during pregnancy< Read More Here /p>
By taking these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing periodontal disease and maintain a healthy smile.