Navigating the Future of Organ Transplants via 3D Bioprinting
Introduction
Organ transplantation has been a life-saving medical procedure for countless individuals suffering from organ failure. However, the demand for organs far exceeds the supply, leading to long waiting lists and unfortunate outcomes for many patients. In recent years, the field of 3D bioprinting has emerged as a promising solution to address this critical issue. By utilizing advanced technology, scientists and researchers are now able to create functional human organs using a patient’s own cells. This groundbreaking development has the potential to revolutionize the future of organ transplants and significantly improve the quality of life for patients in need.
What is 3D Bioprinting?
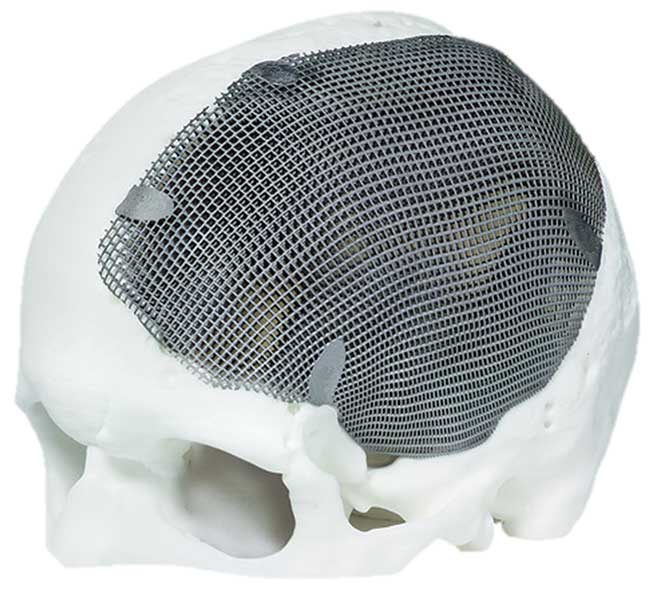
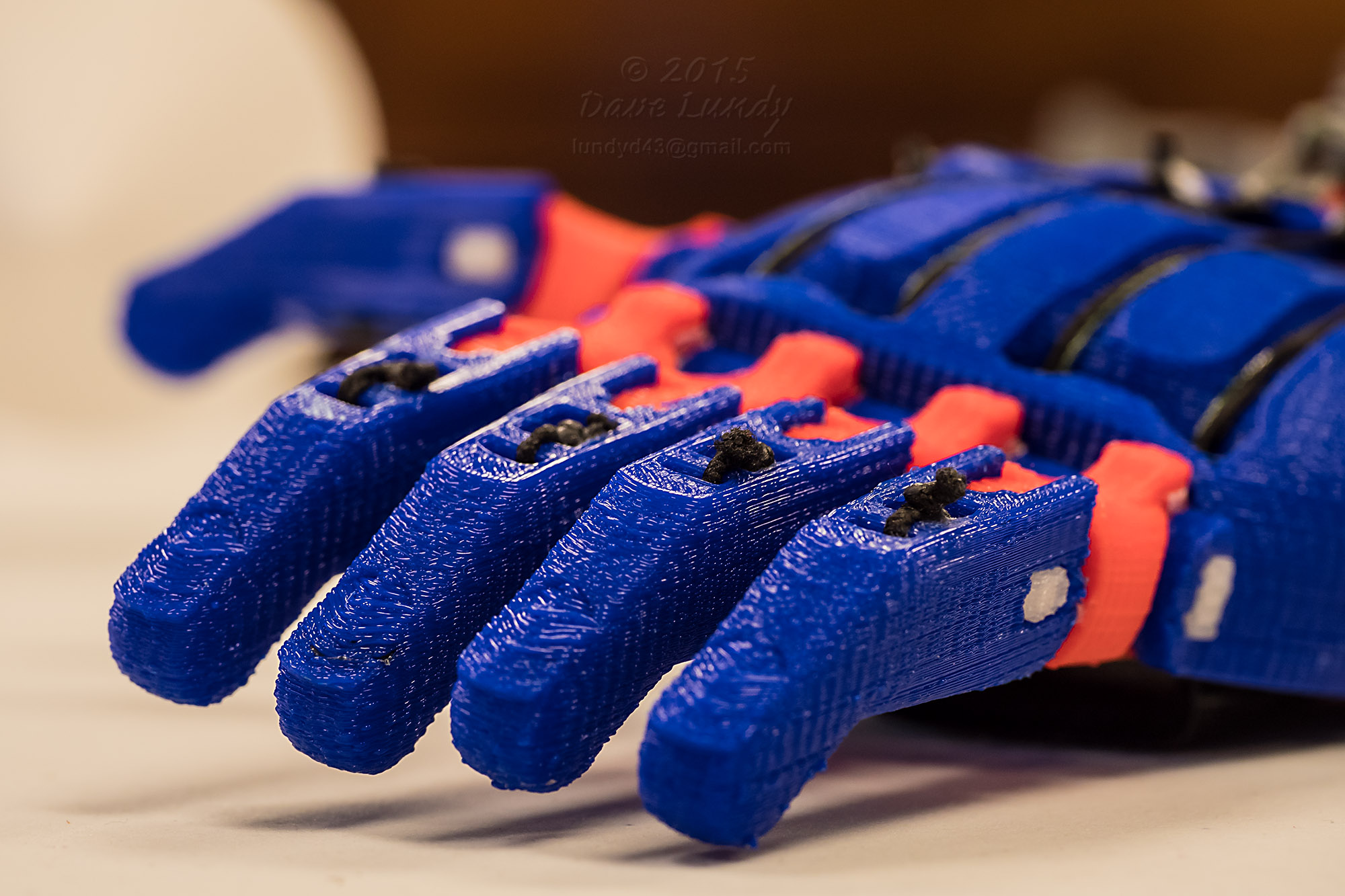
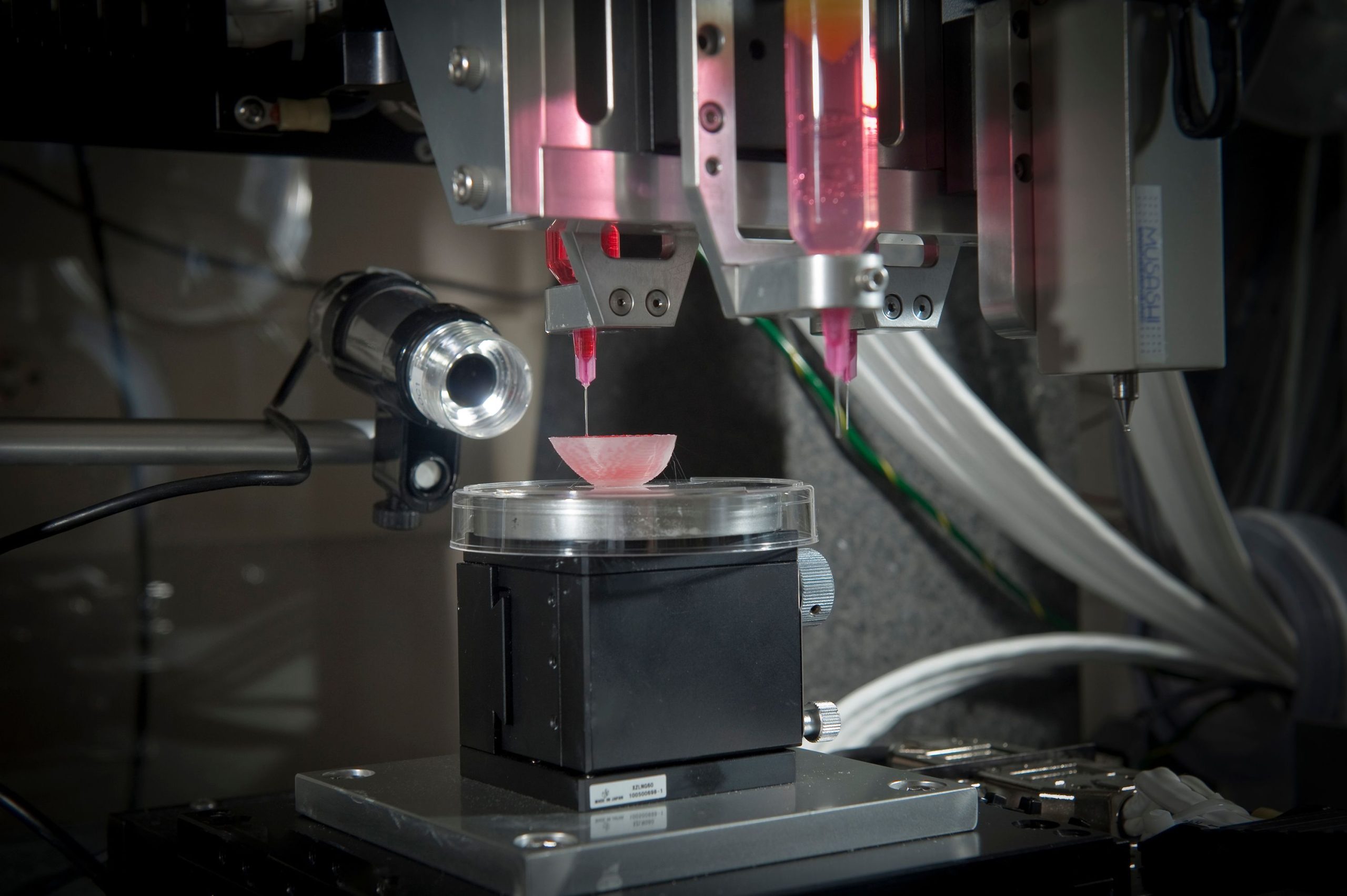
3D bioprinting is an innovative technique that combines 3D printing technology with biology to create functional human organs. It involves the precise layer-by-layer deposition of living cells, biomaterials, and growth factors to construct complex tissue structures. This process mimics the natural architecture of organs, allowing for the creation of organs that are biologically and structurally similar to those found in the human body.
Advantages of 3D Bioprinting
Eliminating the Organ Shortage: One of the most significant advantages of 3D bioprinting is its potential to eliminate the shortage of organs for transplantation. By enabling the creation of organs on demand, this technology could save countless lives and reduce the burden on organ donation programs.
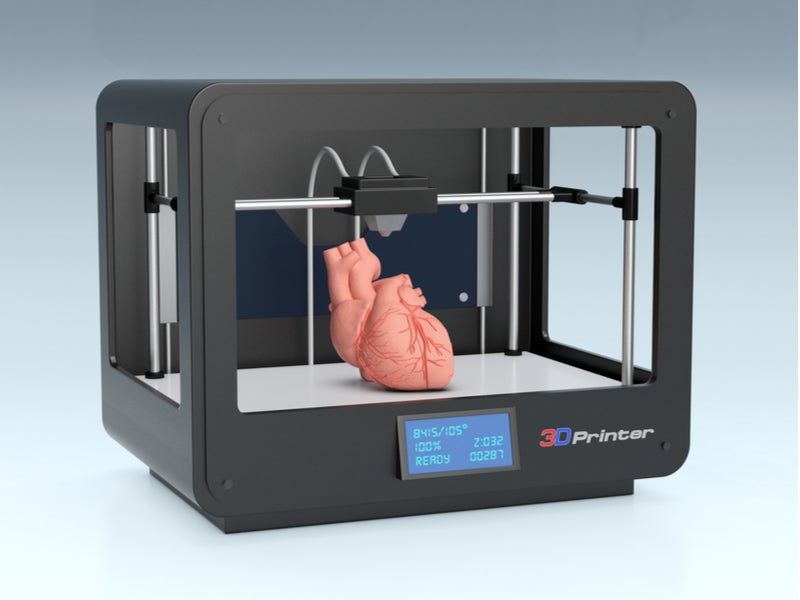
Personalized Medicine: 3D bioprinting allows for the customization of organs based on individual patient needs. This personalized approach ensures a better match between the transplanted organ and the recipient, reducing the risk of rejection and improving overall transplant success rates.
Reduced Waiting Times: With traditional organ transplantation, patients often face long waiting times due to the limited availability of organs. 3D bioprinting has the potential to significantly reduce these waiting times by providing a timely and tailored solution for patients in need.
Summary
3D bioprinting is a cutting-edge technology that enables the creation of complex three-dimensional structures, including human organs, using a layer-by-layer approach. This process involves the precise deposition of bioinks, which are composed of living cells, biomaterials, and growth factors, to build functional tissues and organs. By utilizing a patient’s own cells, the risk of organ rejection is significantly reduced, as the transplanted organ would be genetically identical to the recipient’s body. This personalized approach also eliminates the need for immunosuppressive drugs, which often have severe side effects.
The potential applications of 3D bioprinting in organ transplantation are vast. Currently, researchers are focusing on developing functional prototypes of organs such as kidneys, livers, hearts, and lungs. These organs can be customized to match the specific anatomical and physiological needs of individual patients, ensuring a higher success rate for transplantation procedures. Additionally, 3D bioprinting allows for the creation of organ models for preoperative planning, enabling surgeons to practice complex procedures and optimize surgical outcomes.
While the field of 3D bioprinting is still in its early stages, significant progress has been made, and the future looks promising. However, there are several challenges that need to be addressed before 3D bioprinted organs become a mainstream reality. These include the scalability of the technology, ensuring long-term functionality and viability of the printed organs resource , and regulatory approval processes. Nonetheless, the potential benefits of 3D bioprinting in organ transplantation are undeniable, and continued.
- Q: What is 3D bioprinting?
- A: 3D bioprinting is a revolutionary technology that uses 3D printers to create living tissues and organs by layering bioinks, which are composed of living cells, biomaterials, and growth factors.
- Q: How does 3D bioprinting contribute to organ transplants?
- A: 3D bioprinting offers a potential solution to the shortage of organ donors by enabling the creation of functional organs using a patient’s own cells, reducing the risk of rejection and the need for immunosuppressive drugs.
- Q: What are the advantages of 3D bioprinting in organ transplants?
- A: Some advantages include personalized organ production, reduced waiting times for transplants, elimination of organ rejection, and the ability to create complex structures with precise control over shape and composition.
- Q: Are 3D bioprinted organs currently being used in transplants?
- A: While 3D bioprinting has shown promising results in laboratory settings, it is still in the early stages of development and has not yet been widely used in human transplants. Extensive research and testing are still required before it can be implemented on a larger scale.
- Q: What are the challenges in 3D bioprinting organs for transplants?
- A: Some challenges include the need for biocompatible materials, vascularization of printed tissues, ensuring proper functionality of the printed organs, and regulatory approval for clinical use.
- Q: How long until 3D bioprinted organs become a reality for transplants?
- A: The timeline for the widespread use of 3D bioprinted organs in transplants is uncertain. It depends on the progress of research, overcoming technical challenges, regulatory approvals, and ensuring the safety and efficacy of the technology.