Introduction
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It is caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to serious complications, including tooth loss and systemic health problems. Understanding the stages of gum disease and the available treatment options is crucial for maintaining good oral health.
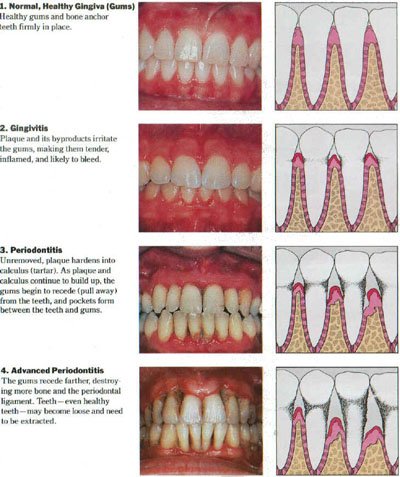
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease. It is characterized by inflammation of the gums, which may appear red, swollen, and bleed easily. At this stage, the damage is reversible, as it only affects the gums and has not yet reached the underlying bone and tissues. Proper oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings, can help reverse gingivitis.
Early Periodontitis
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to early periodontitis. In this stage, the infection spreads below the gum line, causing the gums to recede and form pockets. Bacteria and plaque accumulate in these pockets, leading to further inflammation and damage. The bone and connective tissues that support the teeth may start to deteriorate. Scaling and root planing, a deep cleaning procedure, is often recommended to remove plaque and tartar from the pockets and promote gum healing.
Moderate Periodontitis
Moderate periodontitis is characterized by significant gum and bone damage. The pockets become deeper, allowing more bacteria to accumulate. The gums may recede further, and the teeth may become loose or shift. In addition to scaling and root planing, more advanced treatments such as gum grafting or bone grafting may be necessary to restore the damaged tissues and stabilize the teeth.
Advanced Periodontitis
Advanced periodontitis is the most severe stage of gum disease. The supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone and connective tissues, are extensively damaged. The teeth may become very loose or even fall out. Treatment options at this stage may include tooth extraction, dental implants, or periodontal surgery to remove.
Summary
Gum disease progresses through different stages, each with its own set of symptoms and treatment approaches. The initial stage is known as gingivitis, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. With proper oral hygiene and professional dental care, gingivitis can be reversed. However, if left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, where the infection spreads below the gum line and damages the supporting tissues and bone. Advanced periodontitis is the most severe stage, leading to tooth loss and requiring extensive treatment.
Treatment options for gum disease depend on the stage and severity of the condition. Non-surgical treatments, such as scaling and root planing, are often recommended for early stages. These procedures involve deep cleaning of the teeth and gums to remove plaque and tartar buildup. In more advanced cases, surgical interventions like flap surgery or bone grafting may be necessary to repair the damaged tissues and restore oral health.
Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and a healthy lifestyle are essential for preventing and managing gum disease. By understanding the stag es and treatment options available, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain their oral health and prevent the progression of gum disease.
- Q: What is gum disease?
- A: Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that surround and support the teeth.
- Q: What are the stages of gum disease?
- A: Gum disease has three main stages: gingivitis, periodontitis, and advanced periodontitis.
- Q: What is gingivitis?
- A: Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums.
- Q: What is periodontitis?
- A: Periodontitis is the second stage of gum disease, where the infection starts to damage the bone and connective tissues that hold the teeth in place.
- Q: What is advanced periodontitis?
- A: Advanced periodontitis is the most severe stage of gum disease, causing significant bone loss and potential tooth loss.
- Q: How is gum disease treated?
- A: Treatment options for gum disease include professional dental cleanings, scaling and root planing, medication, and in severe cases, surgery.
- Q: Can gum disease be prevented?
- A: Yes, gum disease can be prevented by practicing good oral hygiene, such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.

Welcome to my website! My name is Lucas Bryce, and I am a dedicated professional Holistic Dentist with a passion for providing exceptional dental care. With years of experience in the field, I am committed to helping my patients achieve optimal oral health and beautiful smiles.