Introduction
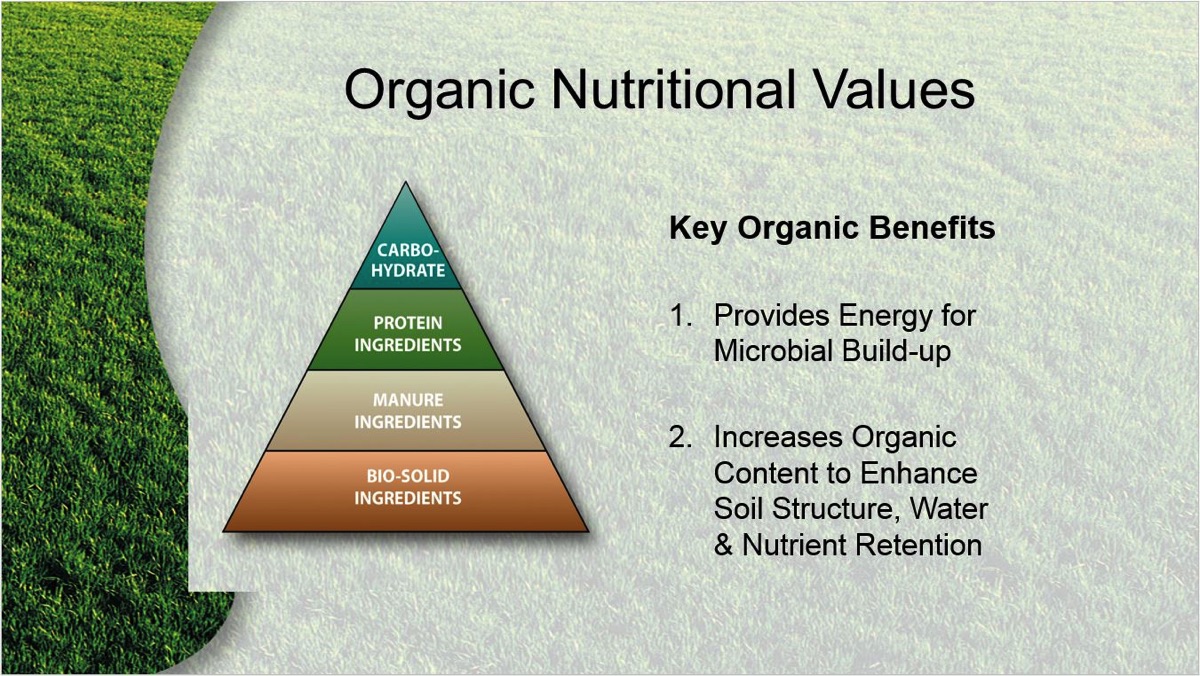
Soil health is crucial for the growth and development of plants. It provides essential nutrients, water, and support to the roots. Organic fertilizers play a vital role in maintaining and improving soil health. Unlike synthetic fertilizers, organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources and provide numerous benefits to the soil ecosystem.
1. Enhancing Soil Structure
Organic fertilizers improve soil structure by increasing its ability to hold water and nutrients. They contain organic matter, such as compost, manure, and plant residues, which act as binding agents. These binding agents help create aggregates, improving soil porosity and reducing compaction.
2. Nutrient Availability
Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly and steadily, ensuring a continuous supply to plants. They contain a wide range of essential nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with micronutrients. These nutrients are released through microbial activity, making them readily available to plants.
2.1 Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a vital nutrient required for plant growth. Organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, contain organic forms of nitrogen that are gradually converted into plant-available forms by soil microorganisms. This slow release of nitrogen reduces the risk of leaching and ensures its efficient utilization by plants.
2.2 Phosphorus
Phosphorus is essential for root development, flowering, and fruiting. Organic fertilizers, such as bone meal and rock phosphate, contain organic forms of phosphorus that are slowly released into the soil. This slow release ensures a steady supply of phosphorus to plants, promoting their overall growth and productivity.
2.3 Potassium
Potassium is crucial for plant metabolism, water regulation, and disease resistance. Organic fertilizers, such as wood ash and kelp meal, provide potassium in organic forms that are gradually released into the soil. This slow release ensures a continuous supply of potassium to plants, enhancing their overall health and vigor.
3. Improving Soil Fertility
Organic fertilizers enhance soil fertility by replenishing organic matter.
Summary
Organic fertilizers offer numerous advantages for soil health and sustainable agriculture. They provide a balanced and slow-release supply of nutrients, ensuring long-term plant growth and productivity. Additionally, organic fertilizers improve soil structure, enhancing water retention and reducing erosion. They also promote the growth of beneficial soil microorganisms, which aid in nutrient cycling and disease suppression. Furthermore, the use of organic fertilizers reduces the risk of chemical runoff and pollution, contributing to a healthier environment. By incorporating organic fertilizers into agricultural practices, farmers can maintain soil fertility, increase crop yields, and support long-te see page rm sustainability.

- Q: What are organic fertilizers?
- A: Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources such as plant and animal waste, and they provide essential nutrients to plants in a slow-release form.
- Q: How do organic fertilizers improve soil health?
- A: Organic fertilizers enhance soil structure, increase microbial activity, improve water retention, and promote nutrient cycling, leading to healthier and more productive soil.
- Q: What are the benefits of using organic fertilizers?
- A: Organic fertilizers improve soil fertility, reduce the risk of nutrient leaching, minimize environmental pollution, and support sustainable agriculture practices.
- Q: Are organic fertilizers safe for the environment?
- A: Yes, organic fertilizers are environmentally friendly as they are biodegradable, do not contain harmful chemicals, and promote long-term soil health without causing pollution or harm to ecosystems.
- Q: Can organic fertilizers be used in all types of soil?
- A: Yes, organic fertilizers can be used in various soil types, including sandy, loamy, and clay soils. They help improve soil structure and fertility regardless of the soil’s composition.
- Q: How often should organic fertilizers be applied?
- A: The frequency of organic fertilizer application depends on factors such as plant nutrient requirements, soil conditions, and crop rotation. It is recommended to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer or consult with a local agricultural expert.
- Q: Can organic fertilizers replace synthetic fertilizers entirely?
- A: While organic fertilizers are beneficial for soil health, they may not provide all the necessary nutrients in the required quantities. A combination of organic and synthetic fertilizers can be used to achieve optimal plant nutrition and sustainable soil management.

Welcome to my website! My name is William Langwell, and I am a dedicated and passionate Home Improvement Contractor with a strong focus on lawn and garden care, eco trash can cleaning, organic fertilizers, and cleaning solutions. With years of experience in the industry, I have honed my skills and expertise to provide top-notch services to homeowners like you.