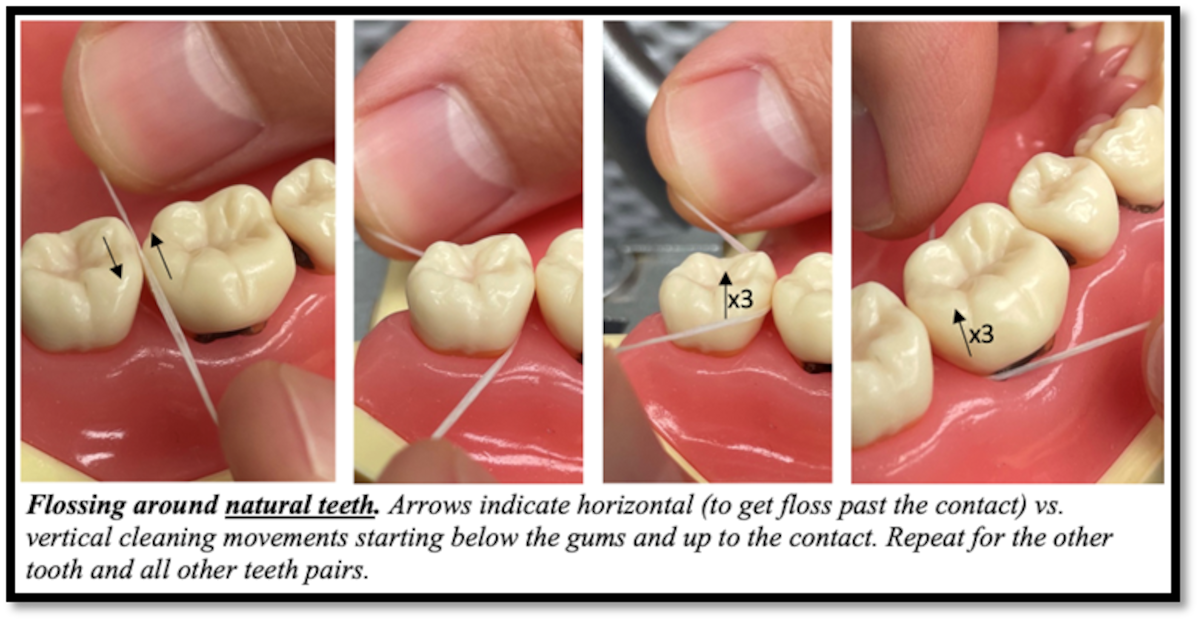
Introduction
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums, which can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. However, recent research has shown that gum disease is not only a threat to oral health but also has a significant impact on overall heart health. The link between gum disease and heart disease has been established, highlighting the importance of preventive strategies to maintain both oral and cardiovascular well-being.
Understanding the Connection
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health issue that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It is caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and other serious complications.
_max_bytes(150000)_strip_icc()/ways-to-prevent-congestive-heart-failure-3859866-Final-618f35bb132a421cbaf6f49a4077c9de.jpg)
Recent research has shown a strong link between gum disease and heart health. Studies have found that people with gum disease are at a higher risk of developing heart disease compared to those with healthy gums. The exact reason behind this connection is still being studied, but several theories have been proposed.
The Role of Inflammation
Inflammation is believed to be a key factor in the link between gum disease and heart health. When gum disease is present, the body’s immune system responds by releasing inflammatory chemicals. These chemicals can enter the bloodstream and contribute to the development of inflammation in other parts of the body, including the arteries.
Arterial inflammation is a known risk factor for heart disease. It can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries, which can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes. By reducing inflammation in the gums, it may be possible to lower the risk of heart disease.
Prevention Strategies
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
The most effective way to prevent gum disease is to practice good oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash to kill bacteria. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are also essential for maintaining gum health.
Quit Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease and heart disease. It weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections like gum disease. Quitting smoking can significantly improve both oral and heart health.
Eat a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support gum and heart health. Avoiding sugary and processed foods can also reduce the risk of gum disease and heart disease.
Summary
Gum disease and heart disease share common risk factors such as smoking, poor oral hygiene, and certain systemic conditions like diabetes. The bacteria present in gum infections can enter the bloodstream and contribute to the development of cardiovascular problems. Studies have shown that individuals with gum disease are at a higher risk of developing heart disease, experiencing heart attacks, and suffering from other cardiovascular complications. Therefore, it i linked here s crucial to adopt preventive strategies to maintain good oral health and reduce the risk of gum disease and its potential impact on heart health.
- Q: What is the link between heart health and gum disease?
- A: Research suggests that there is a connection between gum disease (periodontitis) and heart health. The bacteria present in gum disease can enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation, which may contribute to the development of heart disease.
- Q: How can I prevent gum disease?
- A: To prevent gum disease, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene practices. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, using mouthwash, and visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
- Q: Are there any lifestyle changes that can help prevent gum disease?
- A: Yes, certain lifestyle changes can help prevent gum disease. Avoiding tobacco products, eating a balanced diet, reducing stress, and exercising regularly can all contribute to better gum health.
- Q: Can gum disease be reversed?
- A: In its early stages, gum disease (gingivitis) can be reversed through proper oral hygiene. However, if it progresses to periodontitis, it can only be managed and not completely reversed. Seeking professional dental treatment is crucial in managing gum disease.
- Q: How often should I visit the dentist to prevent gum disease?
- A: It is recommended to visit your dentist every six months for regular check-ups and cleanings. However, your dentist may suggest more frequent visits if you are at a higher risk of developing gum disease.

Hello, I’m Brock Pattison, a dedicated professional in the field of Gum Disease Prevention and Oral Health. With a passion for helping individuals achieve optimal oral hygiene, I am committed to providing valuable information and resources to promote healthy smiles.