Introduction
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, and this includes the health of our teeth and gums. The food we consume not only affects our physical well-being but also has a significant impact on the development of oral diseases. In this blog post, we will explore how your diet can influence the development of oral diseases and the importance of making healthy dietary choices for optimal oral health.
The Link Between Diet and Oral Health
When it comes to maintaining good oral health, most people focus on brushing and flossing regularly. However, what you eat also plays a crucial role in the development of oral diseases. Your diet directly impacts the health of your teeth and gums, and making the right food choices can help prevent various oral issues.
Sugar and Tooth Decay
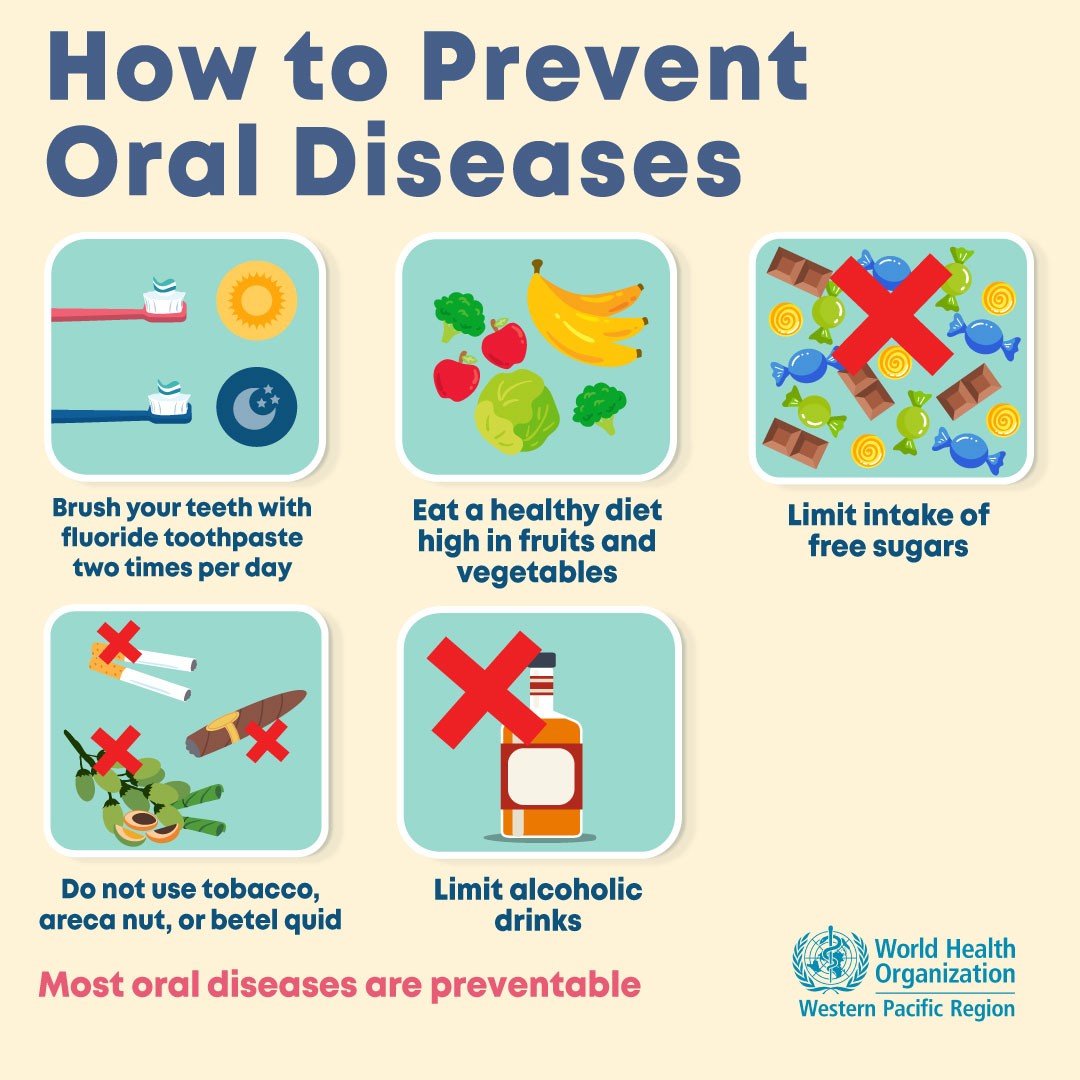
One of the primary culprits behind oral diseases is sugar. Consuming excessive amounts of sugar can lead to tooth decay. Bacteria in your mouth feed on sugar and produce acids that attack the enamel, causing cavities. Limiting your sugar intake, especially from sugary drinks and snacks, can significantly reduce the risk of tooth decay.
Acidic Foods and Erosion
Acidic foods and beverages, such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, and carbonated drinks, can erode the enamel over time. Acid weakens the protective layer of your teeth, making them more susceptible to decay and sensitivity. It’s important to consume acidic foods in moderation and rinse your mouth with water afterward to neutralize the acid.
Calcium and Strong Teeth
Calcium is essential for maintaining strong teeth and bones. A diet rich in calcium helps prevent tooth decay and keeps your teeth healthy. Include dairy products, leafy greens, almonds, and fortified foods in your diet to ensure an adequate intake of calcium.
Vitamin C and Gum Health

Vitamin C plays a vital role in maintaining healthy gums. Deficiency in this vitamin can lead to gum diseases like gingivitis and periodontitis. Include citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli in your diet to boost your vitamin C intake and promote gum health.
Water and Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health, including oral health. Drinking water helps wash away food particles and bacteria, preventing plaque buildup and bad breath. It also stimulates saliva production, which neutralizes acids and protects your teeth. Make sure to drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day.
Summary
Our diet has a direct influence on the health of our teeth and gums. Consuming a diet high in sugar, acidic foods, and processed carbohydrates can contribute to the development of oral diseases such as tooth decay, gum disease, and enamel erosion. These types of foods provide an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to thrive, leading to the production of acids that attack tooth enamel and cause cavities. Additionally, a lack of essential nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D, can weaken teeth and increase the risk of oral health problems.
On the other hand, a balanced and nutritious diet can help protect and strengthen our teeth and gums. Foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and almonds, promote strong teeth and bones. Vitamin C, found in citrus fruits and vegetables, helps maintain healthy gums and supports the healing process. Crunchy fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, stimulate saliva production, which helps wash away food particles and neutralize acids in the mouth. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day also aids in maintaining oral health by keeping the mouth hydrated and rinsing away bacteria.
It is essential to be mindful of our dietary choices and make conscious efforts to incorporate tooth-friendly foods into our meals. By doing so, we can significantly reduce the risk of oral diseases and maintain a healthy https://dental.buffalo.edu/education/dds-program1/life-and-support.html smile for years to come.
- Q: How can my diet influence the development of oral diseases?
- A: Your diet plays a significant role in oral health. Consuming sugary and acidic foods and beverages can contribute to tooth decay and enamel erosion. Additionally, a lack of essential nutrients can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to gum disease and other oral infections.
- Q: What types of foods and drinks should I avoid to prevent oral diseases?
- A: It is advisable to limit your intake of sugary snacks, carbonated drinks, fruit juices with added sugars, and acidic foods like citrus fruits. These can increase the risk of tooth decay and erosion. Starchy foods that tend to stick to your teeth, such as chips and crackers, should also be consumed in moderation.
- Q: How can I promote good oral health through my diet?
- A: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products can help maintain healthy teeth and gums. Drinking plenty of water, especially fluoridated water, can also aid in preventing oral diseases. Chewing sugar-free gum after meals can stimulate saliva production, which helps neutralize acids and wash away food particles.
- Q: Are there any specific nutrients that are beneficial for oral health?
- A: Yes, several nutrients are essential for maintaining oral health. Calcium and vitamin D are crucial for strong teeth and bones. Vitamin C helps prevent gum disease and promotes gum tissue health. Phosphorus, found in foods like fish and eggs, is important for tooth development and repair. Lastly, antioxidants like vitamin E and beta-carotene can protect oral tissues from damage.
- Q: Can poor nutrition lead to gum disease?
- A: Yes, a diet lacking in essential nutrients can weaken the immune system and make it harder for your body to fight off infections, including gum disease. Vitamin C deficiency, for example, can lead to bleeding gums and slow healing of oral tissues. It is important to maintain a well-balanced diet to support overall oral health.

Welcome to my website! My name is Matthew Bracy, and I am a dedicated professional in the field of periodontal services, holistic dental care, nutrition, and oral health. With a passion for helping others achieve optimal oral well-being, I am committed to providing valuable information and services to enhance your dental health journey.