Introduction
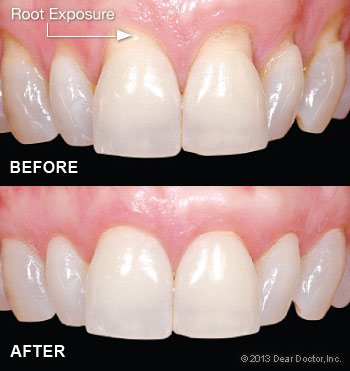
Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, is a common dental condition where the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing the tooth roots. This can lead to tooth sensitivity, increased risk of tooth decay, and even tooth loss if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the causes, treatment options, and the role of gum grafting in addressing receding gums.
Causes of Receding Gums
Several factors can contribute to the development of receding gums:
1. Periodontal Disease
Gum disease, specifically periodontitis, is a leading cause of gum recession. The infection and inflammation associated with periodontal disease can damage the gum tissue and supporting structures, leading to gum recession.
2. Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing can allow plaque and tartar buildup, which can irritate and inflame the gums. Over time, this can contribute to gum recession.
3. Aggressive Brushing
Brushing your teeth too hard or using a toothbrush with hard bristles can cause the gum tissue to wear away gradually. It is important to use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle brushing techniques to avoid damaging the gums.
4. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during pregnancy or menopause, can make the gums more sensitive and prone to recession.
5. Tobacco Use
Smoking or using other tobacco products can impair blood flow to the gums, making them more susceptible to recession.
Treatment Options for Receding Gums
The treatment for receding gums depends on the severity of the condition. Here are some common treatment options:
1. Scaling and Root Planing
This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar buildup from the teeth and root surfaces. It helps to eliminate bacteria and promote gum healing.
Summary
Receding gums can be caused by various factors, including poor oral hygiene, aggressive brushing, gum disease, hormonal changes, and genetic predisposition. It is crucial to identify and address the underlying cause to prevent further gum recession. Treatment options for receding gums range from non-surgical approaches, such as improved oral hygiene practices and professional cleanings, to surgical interventions like gum grafting.
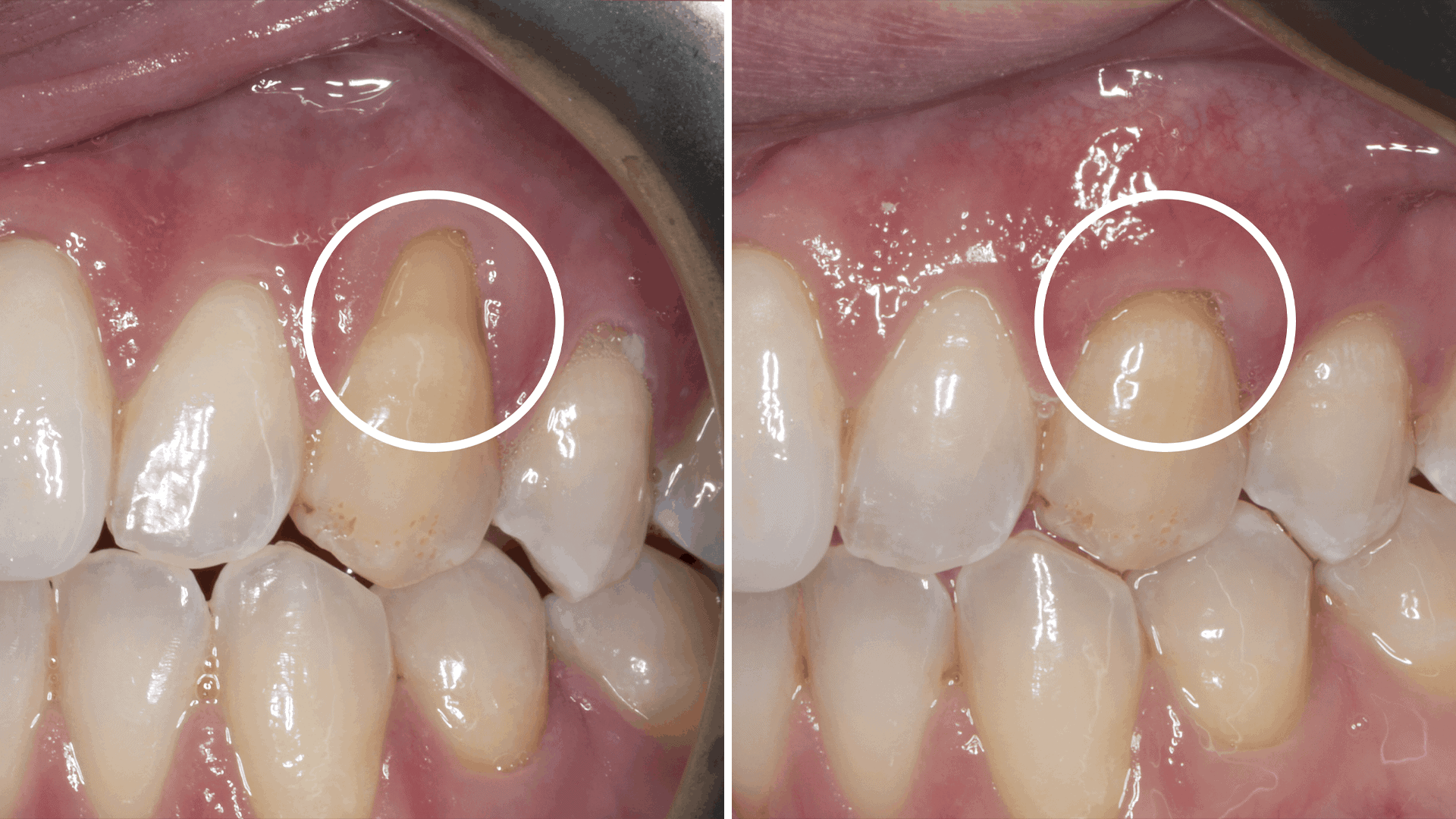
Gum grafting, also known as a gingival graft, is a surgical procedure that involves taking gum tissue from another area of the mouth, such as the palate, and grafting it onto the affected area. This helps to cover the exposed roots, protect them from further damage, and restore a healthy gumline. Gum grafting can be performed using different techniques, including connective tissue grafts, free gingival grafts, and pedicle grafts, depending on the specific needs of the patient.
By understanding the causes of receding gums and exploring the available treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and address this common dental issue. Regular dental check -ups, maintaining good oral hygiene practices, and seeking professional advice are essential for maintaining healthy gums and overall oral health.
- Q: What causes receding gums?
- A: Receding gums can be caused by various factors such as gum disease, aggressive brushing, hormonal changes, tobacco use, and genetic predisposition.
- Q: What are the treatment options for receding gums?
- A: Treatment options for receding gums include deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), antibiotic therapy, gum grafting, regenerative procedures, and lifestyle changes.
- Q: What is gum grafting?
- A: Gum grafting is a surgical procedure where gum tissue is taken from another part of the mouth (or a donor source) and attached to the areas with receding gums to cover the exposed tooth roots.
- Q: How long does it take to recover from gum grafting?
- A: The recovery time for gum grafting can vary, but it generally takes about 1-2 weeks for the initial healing. Complete healing may take several months.
- Q: Are there any risks or complications associated with gum grafting?
- A: Like any surgical procedure, gum grafting carries some risks such as infection, bleeding, swelling, and discomfort. However, these complications are rare and can be minimized with proper post-operative care.
- Q: Can receding gums be reversed without surgery?
- A: In some cases, early-stage gum recession can be treated without surgery by addressing the underlying cause, improving oral hygiene, and using desensitizing toothpaste or mouthwash. However, advanced cases usually require surgical intervention.

Welcome to my website! My name is Noah Keating, and I am a dedicated and passionate Dental Assistant with extensive experience in the field. I am thrilled to share my knowledge and expertise with you through this platform, focusing on topics such as Dental Ethics, Gum Grafting, Toothpaste, and Root Canals.